In the next eight years, the worldwide serverless AI industry is expected to grow to $46.5 billion, according to a report. This is due to the fact that AI is now driving everything from chatbots and customized suggestions to autonomous systems. But applying intelligent models effectively is more difficult than developing them.
Deploying AI models used to require manual resource scaling and complicated infrastructure management. Additionally, it required ongoing workload monitoring to guarantee peak performance. In addition to using time and money, this shifted attention from invention to upkeep.
That’s where serverless AI steps in. It blends the ease of use and adaptability of serverless computing with the intelligence of machine learning. Organizations can now implement AI models that automatically scale and manage erratic workloads by integrating platforms like AWS Lambda.
In this guide, we’ll explore what serverless AI is and how to build auto scaling intelligence using AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions.
Serverless AI
Serverless AI refers to the execution of AI workloads on serverless platforms like Google Cloud Functions and AWS Lambda.
Your model would be installed on a fixed server or container in a traditional setup, and scaling in response to user traffic would be manually controlled. You just implement your AI logic as lightweight functions in serverless computing. These functions automatically execute in response to triggers and scale up or down without any manual intervention.
When no requests are coming in, there are no running servers, meaning zero idle cost. Hundreds or thousands of function instances can operate in parallel to smoothly manage the load as demand surges.
To put it another way, serverless AI enables you to focus on creating intelligent models while your cloud provider handles all the operational tasks, such as fault tolerance and provisioning.
How Serverless AI Works?
Serverless AI typically follows an event driven workflow:
- Trigger: The AI function is triggered by a certain event, such as a message arriving in a queue or a new image uploaded to cloud storage.
- Function Execution: The serverless function loads the AI model and draws conclusions from the analysis.
- Output: In order to take additional action, such as updating a database or starting a different process, the results are either saved or transferred to another service.
How to Build Auto Scaling Intelligence with AWS Lambda?
Understand the Role of AWS Lambda in AI Workloads
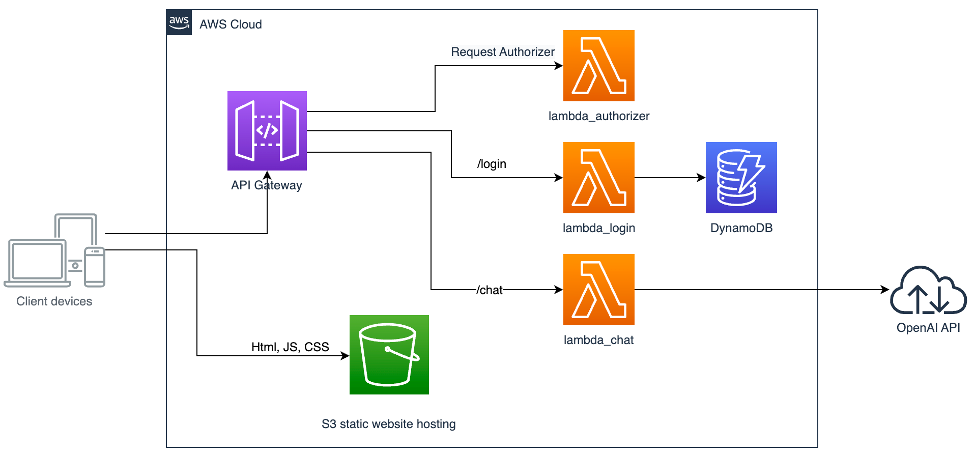
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that runs your code automatically in response to events like API calls and grows based on the amount of incoming requests. It is hence ideal for AI apps with unpredictable workloads.
For example, during business hours, a machine learning model that analyzes consumer sentiment from live chat data may see surges. Lambda ensures cost effectiveness without sacrificing performance by effectively scaling up during peaks and down to zero while idle.
Prepare Your AI Model for Lambda
An AI model must be packed and tuned to fit Lambda’s resource limitations before it can be deployed. Lightweight models or efficient inference engines work well since each function has a limited amount of memory and execution time. To enhance and compress models for quicker inference times, developers frequently utilize programs like Amazon SageMaker.
After the model has been optimized, it should be kept in Amazon S3 so that it may be loaded while it is being executed. Layers like AWS Lambda and NumPy may be utilized to manage dependencies. Layers act as reusable libraries that functions can import, reducing cold start times and simplifying maintenance.
Set Up Event Triggers
The event driven design of AWS Lambda is one of its distinguishing characteristics. AI models can respond to real-time data and external events with ease thanks to lambda functions that are triggered by particular triggers. Amazon API Gateway is a common trigger for AI workloads.
For example, every time a new image is uploaded to an S3 bucket, an image recognition system may automatically do inference. The S3 event triggers the Lambda function. After that, it obtains the picture and analyzes it using a trained model. It then saves the prediction results in a database.
Integrate with Other AWS Services
When Lambda is combined with other AWS ecosystem services, it becomes much more potent and allows for the development of fully functional AI pipelines. Models may be trained or refined using AWS SageMaker, and then served for inference using Lambda. Amazon S3 is used to centrally store datasets and model artifacts.
AWS Step Functions may coordinate many Lambda functions in a series to handle data pretreatment and postprocessing in distinct phases for more intricate processes. Amazon CloudWatch is used for monitoring, including automatic notifications for error tracking and performance analytics.
Deploying and Testing the Lambda Function
The next stage is deployment once the triggers are prepared. Lambda functions may be directly deployed using the AWS Management Console. It is crucial to do adequate testing prior to manufacturing. To guarantee that the function scales smoothly and that inference latency is low under large demand, developers should simulate different traffic patterns.
Managing Concurrency
The capacity of AWS Lambda to automatically grow horizontally is one of its greatest benefits. The system can handle several requests at once since each incoming event starts a new instance of the function. Developers may set up Provisioned Concurrency to reduce cold start times for sensitive apps like chatbots and Reserved Concurrency to guarantee that crucial workloads always have enough resources.
Consider a voice recognition system handling thousands of concurrent requests during business hours. Lambda automatically scales up to manage the surge and then scales back down when demand decreases, eliminating idle costs.
Implementing AI with Google Cloud Functions

Google Cloud Functions is a fully managed and event driven platform that automatically runs your code in response to events from various Google services, such as Cloud Storage or even external HTTP requests. It’s a serverless compute solution, meaning you don’t have to manage servers or scaling logic.
In the context of AI, Cloud Functions serve as the deployment layer for lightweight inference tasks, allowing developers to trigger predictions or data processing directly from events. For instance, a Cloud Function can instantly use a pre trained image classification model from Vertex AI when a user uploads a photo to Cloud Storage.
Prepare Your AI Model for Cloud Functions
Make sure your model is tuned for effective inference before implementing AI with Cloud Functions. Since Cloud Functions are designed for short lived and stateless operations, models should be simplified or hosted externally.
Here’s how to prepare your model for deployment:
- Model Optimization: To convert your model into a lightweight format, use applications such as ONNX or TensorFlow Lite. This ensures faster load times.
- Storage Setup: Store your trained model in Google Cloud Storage. Cloud Functions can easily fetch it at runtime when invoked.
- Dependency Management: Include necessary Python or Node dependencies in your deployment package file.
- Environment Configuration: Use environment variables in Cloud Functions to manage API keys or configuration parameters securely.
Set Up Necessary Event Triggers
One of the biggest strengths of Cloud Functions is its event driven architecture. This implies that certain occurrences in your Google Cloud environment may automatically initiate your function. You may configure several sorts of triggers based on your use case.
A Cloud Storage trigger is perfect for applications like document scanning and image analysis since it may call a function whenever fresh data is uploaded. For streaming data or real time forecasts, a Pub/Sub trigger can initiate your function anytime a message enters a topic. Additionally, an HTTP trigger enables real time inference for web and mobile apps by exposing your AI function as a RESTful API endpoint. Lastly, a Firestore trigger may react to database changes, enabling real time analysis or forecasts depending on user input.
Integrating AI with Google Cloud Services
Numerous services in the Google Cloud ecosystem may be connected using Google Cloud Functions. Developers may create clever processes that smoothly link data collecting and analytics thanks to this connectivity.
Additionally, Google offers pre trained APIs that are simple to use within Cloud Functions, such Vision and Natural Language. This enables sophisticated AI features like object identification while removing the requirement to train models from scratch.
Deploying and Testing Cloud Functions
You may use the Google Cloud Console to immediately deploy your function after your model and integrations are complete. You select the function’s runtime and trigger type during deployment.
It is also essential to fully test the feature under all circumstances before going live. Before deploying the function, you may test it locally using the Cloud Functions emulator to make sure it operates as expected. After deployment, performance parameters like execution time may be monitored using cloud logging. To make sure the function scales well under heavy demand, developers may also do load tests by simulating numerous data uploads or API requests.
Managing Performance
The automated scalability of Google Cloud Functions is one of its most attractive features. In order to accommodate incoming requests, the platform may instantaneously construct numerous instances of your function, guaranteeing continuous performance regardless of traffic amounts.
To further optimize scaling, you can apply techniques such as cold start migration, which involves reducing dependencies and keeping the function lightweight. Redis may also be used to create caching, which reduces unnecessary processing by storing frequently used data or preloded models.
In addition to using Cloud Trace and Cloud Profiler to track latency and locate performance bottlenecks, developers may regulate concurrency levels to prevent overloading downstream systems or APIs.
Best Practices for Serverless AI Development
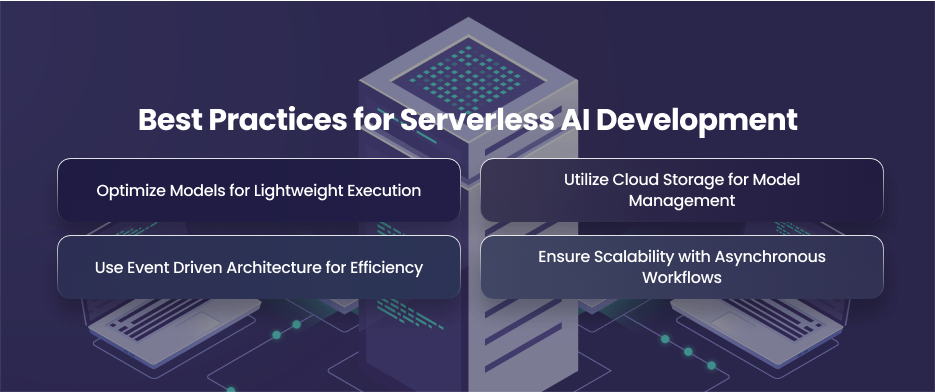
Optimize Models for Lightweight Execution
Strict memory and execution time restrictions apply to serverless systems like AWS Lambda. AI models need to be tuned for lightweight execution in order to function well under these constraints. To minimize model size without appreciably sacrificing accuracy, developers might employ model comparison strategies like quantization or knowledge distillation.
For example, TensorFlow is an excellent tool for converting heavy models into smaller and server less compatible versions. A smaller model not only loads faster but also reduces cold start delays and runtime costs. Additionally, using pre trained models for common tasks can save both development time and computational resources.
Utilize Cloud Storage for Model Management
Instead of embedding large models directly into the function, it’s more efficient to store them in a cloud infrastructure. So, when a functions is triggered, it can load the model from storage on demand. This approach reduces deployment size and allows for easy model updates without redeploying the function.
In order to prevent reloading models on each call, developers should additionally use caching techniques. You may drastically reduce latency and resource usage by storing frequently used data and models in memory during concurrent runs.
Use Event Driven Architecture for Efficiency
Serverless AI works best when it follows an event driven model. Additionally, functions should be made to respond to particular triggers, such an API request or a fresh file upload. This guarantees that resources are used only when necessary, resulting in effective AI processes.
For example, a language model may do sentiment analysis on social media data streams in real time, or an image recognition model can be automatically activated each time a new image is uploaded to cloud storage. In addition to providing on demand AI intelligence that dynamically adapts with consumption patterns, this design minimizes idle server expenditures.
Ensure Scalability with Asynchronous Workflows
Effective serverless AI scalability requires asynchronous processing. Functions should use message queues like AWS SQS to process requests asynchronously rather than waiting for each job to be finished.
Because of this, several AI tasks may be performed simultaneously without creating bottlenecks. Additionally, it guarantees that operations are resistant to traffic spikes. Moreover, they sustain good throughput even in the face of demanding workloads.
Final Words
Developers can build intelligent, self scaling systems without worrying about infrastructure maintenance thanks to serverless AI. By combining optimized models with cloud native technology, organizations may achieve efficiency.





