According to Fortune Business Insights, the global MLOps market size will increase to $19. 55 billion in the next seven years. This is due to the fact that ML models are changing the way that companies make choices. But creating a model in a lab and getting it to function well in a real-world setting are two whole different issues.
MLOps can be useful in this situation. MLOps simplifies the deployment and upkeep of ML models by fusing the concepts of DevOps with machine learning. It guarantees a seamless and repeatable transition from experimental to production.
We will go over what MLOps is and why it is crucial to the development of contemporary AI in this guide. In addition, we’ll also discuss the most efficient ways to put it into practice.
MLOps
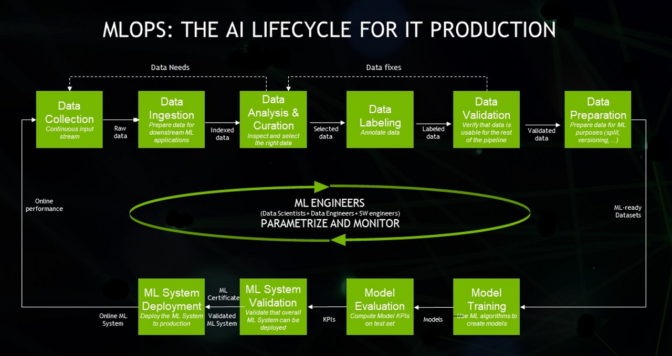
By merging the ideas of DevOps and machine learning, MLOps enhances the whole lifecycle of ML models, from early testing to deployment.
Data scientists concentrate on creating and training models in conventional machine learning processes, frequently operating in remote settings with local datasets and unique scripts. The problem that arises when a model is prepared is how to put it into production.
Fundamentally, MLOps gives ML processes automation and standardization. DevOps served as its inspiration. However, MLOps extends these ideas to handle the unique complexities of ML systems.
Unlike traditional software, ML models are data driven and dynamic. Their performance depends not only on the code but also on constantly changing data and model parameters.
Why MLOps Matters in Modern AI Development?

Bridging the Gap Between Data Science and Operations
The gap between operations and data science teams is one of the primary obstacles to machine learning’s growth. System security is the first priority for DevOps engineers and IT teams, while data scientists concentrate on experimentation and model creation.
MLOps connects these teams by offering a standardized platform for effective cooperation. It also provides a standard language and process for integrating machine learning models into existing production systems. This alignment guarantees that models created in research settings work flawlessly in practical applications and lowers friction.
Managing the Complexity of ML Pipelines
Machine learning workflows involve multiple interconnected stages. These include:
- Data Ingestion
- Feature Engineering
- Model Training
- Validation
- Deployment
- Training
Each stage relies on different tools and often requires continuous iteration as data changes. Additionally, MLOps introduces process orchestration and pipeline automation to simplify this complexity. By automating these processes, MLOps ensures consistency and makes result replication easier. This degree of organization turns the development of machine learning from a collection of haphazard attempts into a dependable procedure.
Reproducibility
The legitimacy of machine learning depends on its reproducibility. The outcome of a model must be reproducible by teams utilizing identical data. However, without proper version control, this is nearly impossible.
MLOps enforces rigorous versioning for data and models, ensuring every experiment is tracked. Tools like DVC and MLflow record changes to datasets and training environments, allowing teams to easily roll back or revalidate models when needed.
Accelerating Model Deployment
Under normal circumstances, it may take weeks or even months to update an old model or put a new one into place. The primary reasons for delays are manual handoffs.
Machine learning specific pipelines for deployment and continuous integration are used by MLOps. These pipelines allow teams to submit changes to production more often by automating model testing. This agility is very beneficial to businesses since it allows them to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
Sustaining Model Performance Over Time
Model drift is the term used to describe how machine learning models become less accurate and relevant when real world data changes. For instance, a credit risk model trained on last year’s data might perform poorly as new economic conditions emerge.
MLOps introduces continuous monitoring to track model performance post deployment. If the accuracy of a model decreases or input data changes significantly, the system can quickly trigger alerts or begin retraining operations. This continuous feedback loop makes sure that models remain reliable and consistent with current data patterns, which lessens the risks associated with outdated projections.
Managing several models across different teams, use cases, and settings gets more difficult as businesses expand their AI activities. Hundreds Enhancing Scalability
of models may be deployed and maintained concurrently with the help of MLOps’ scalable architecture.
MLOps lowers the operational overhead of growing AI systems by centralizing model administration and automating procedures. It guarantees that resources are distributed wisely and that new models may be implemented rapidly.
Supporting Governance and Ethical AI
Strict laws and moral principles must be followed by AI apps. To guarantee that models are comprehensible and adhere to data protection regulations, MLOps implements structured governance.
Model lineage tracking is made possible by it, which records the data utilized and the deployment date. Building accountability in AI systems and ensuring that model judgments can be supported by evidence and audited when necessary depend on this openness.
Components of MLOps
Data Management
The effectiveness of AI systems is directly influenced by the caliber, applicability, and accessibility of data. Data management in MLOps makes ensuring that data pipelines are dependable and adhere to legal and organizational requirements.
Effective data management involves:
- Data Versioning: Monitoring several iterations of the training and validation datasets. This enables teams to evaluate model performance across different data snapshots and replicate trials. For this, Delta Lake and similar tools are frequently utilized.
- Data Validation: Automated checks are made to make sure incoming data is consistent and clean before models are trained. Performance deterioration and downstream mistakes are avoided with the use of these validation procedures.
- Data Drift Detection: Real world data constantly changes. MLOps systems include monitoring mechanisms that detect when the characteristics of production data deviate from the training data, a process known as data drift. Detecting drift early helps trigger retraining workflows proactively.
- Data Governance: With more stringent privacy laws, MLOps implements data governance procedures that guarantee data use conforms to moral and legal requirements.
Model Development
Data scientists test several algorithms, adjust hyperparameters, and conduct tests throughout the model development process in order to determine which model performs the best. This procedure may easily devolve into chaos in conventional processes, with a large number of untracked tests and uneven outcomes.
Furthermore, MLOps brings structure to this phase through:
- Experiment Tracking: Tools like MLflow record details about every experiment. As a result, this facilitates results comparison and cross team sharing.
- Reusable Pipelines: MLOps employs reusable pipelines that standardize processes like preprocessing and model training in place of manually rerunning trials. This ensures consistency and saves time.
- Collaborative Development: Collaboration between DevOps experts and data scientists is encouraged by MLOps platforms. Version control systems and shared environments facilitate conflict avoidance.
- Automated Testing: During development, automated unit tests validate code quality and model logic to catch errors early.
Model Deployment
A model must be put into a real world setting once it has been trained and verified in order for it to produce insights. This stage, known as model deployment, is one of the most complex yet crucial components of MLOps.
By automating the packaging and integration of models into production systems, MLOps streamlines deployment. Docker and other containerization technologies guarantee that models and their dependencies function flawlessly in a variety of settings.
Furthermore, real time predictions at scale are frequently made possible by model serving frameworks like TensorFlow. Deployment techniques like A/B testing also enable teams to test model performance in production without affecting users.
Model Monitoring
Models may become less accurate over time as a result of shifting user behavior. Model maintenance and monitoring are crucial elements of MLOps in this situation. By tracking parameters like accuracy and error rates, continuous monitoring guarantees that models operate consistently.
In order to identify departures from anticipated patterns, data drift and concept drift detection algorithms continually examine incoming data and predictions. Therefore, automatic retraining processes may be set up to update the model with fresh data and redeploy it when performance falls below a predetermined level.
In order to preserve transparency and traceability, logging and auditing are also essential. They record each forecast and system occurrence. Debugging and comprehending long term model behavior are made much easier with the help of these logs.
Compliance and Security
Every facet of model creation and deployment complies with legal and ethical requirements thanks to MLOps’ compliance and security component. From data sources and training settings to production deployment and upgrades, model lineage tracking keeps an exhaustive record of each model’s history.
For audits and accountability, this degree of traceability is essential. To safeguard data and stop illegal access to models or systems, MLOps additionally uses encryption protocols and role based access.
Best Practices for Successful MLOps Implementation

Start with a Strong Data Foundation
The foundation of any machine learning effort is data. In the absence of clean and consistent data, even the most advanced MLOps frameworks will fail.
Data versioning, which guarantees that all datasets used for training and testing are recorded and repeatable, is the first step in building a strong data foundation. All datasets used for training and testing are recorded and repeatable when data quality checks and validation procedures are put in place. Models are always trained on dependable inputs thanks to the implementation of validation pipelines and data quality checks.
Clear data governance principles also help to avoid privacy problems and noncompliance with regulations. Teams can create and implement accurate models with confidence when the data layer is well structured.
Automate the ML Pipeline
Manual procedures raise the possibility of human mistakes and impede innovation. Automation is an essential component of MLOps for the effective extension of AI operations.
Automating the machine learning pipeline involves using tools and scripts to handle repetitive tasks like data preparation. Machine learning specific deployment pipelines make sure that automated procedures validate and deploy updates without any problems when a model or dataset changes.
Integrate Version Control
Git and other version control systems are used in conventional software development to monitor code changes. This idea must be applied to datasets and configuration files in MLOps, though.
Tools like DVC make it easy to track every experiment and parameter adjustment. This means if performance drops or errors occur, teams can quickly roll back to a previous stable version.
Continuously Monitor Model Performance

Metrics like input data distribution and forecast accuracy require constant observation. Additionally, teams may utilize technologies like Prometheus to monitor and notify them of performance decline.
Additionally, MLOps teams should set up KPIs that align with business goals. This includes monitoring the precision of fraud detection or customer attrition predictions. Automated retraining procedures can guarantee that the model continues to be relevant when anomalies are found.
Implement Scalable Infrastructure
A flexible and scalable infrastructure is necessary to manage several models and large datasets as AI use increases. Managed services offered by AWS SageMaker and other cloud platforms improve resource allocation and deployment.
Kubernetes and other orchestration and containerization platforms enable effective scaling. This guarantees that models may manage different workloads without experiencing any performance issues.
Final Words
By linking operations and data science, MLOps improves the whole machine learning lifecycle. MLOps uses process automation to transform AI from experimental models into production ready solutions.