Mind Inventory reports that the global IT spending is expected to rise at a CAGR of 22.5%, with a revenue forecast of $146.18 billion. This is because software development now is much more than writing code. It’s about building high quality efficiently and with minimal risk. Software development approaches are therefore crucial for this reason.
Your development strategy may make or destroy your project, regardless of whether you’re creating an enterprise grade platform or a basic app. Additionally, each methodology offers a unique way to plan and manage software development. Choosing the appropriate one is therefore crucial to ensuring that your team works well.
So, in this guide, we will discuss 10 software development methodologies and why they matter.
What is a Software Development Methodology?
A software development methodology is a structured procedure or framework that directs the planning of software projects. It also contains a set of guidelines that development teams adhere to in order to create software effectively.
Moreover, these approaches are not only theoretical; they offer practical advice on how to organize work at every phase in the lifecycle of software development.
At its core, a methodology defines how a team approaches the stages of software development, including:.
- Requirement gathering
- Design and architecture
- Coding and implementation
- Testing and quality assurance
- Deployment and release
- Maintenance and support
Elements of a Software Development Methodology
- Process Structure: It describes the steps a project should take, whether in iterative cycles or a sequential flow.
- Team Roles: It specifies how developers and project managers work together as well as who is responsible for what.
- Tools: It may prescribe the use of certain tools for version control and automation.
- Deliverables: These outputs, such as final code or prototypes, are anticipated at every stage of the development cycle.
- Feedback: Certain approaches have planned moments for introspection, enabling the process to evolve in response to market needs.
Why Development Teams Adhere to a Software Development Methodology?

Improved Project Clarity
Software projects often involve dozens of tasks. Therefore, anarchy may swiftly take control in the absence of a defined structure. Furthermore, by segmenting the project into organized stages, a software development methodology contributes to the establishment of order. Whether it’s planning or deploying, each step has defined inputs and expected outputs.
This structure helps the team:
- Avoid overlooked tasks or duplicated efforts
- Align on goals and timelines from the outset
- Easily manage complex projects with multiple dependencies
Enhanced Communication
Software development is a team driven effort that demands close collaboration between developers and designers. Also, methodologies create a shared system for how team members interact and report progress.
For example:
- Agile provides daily stand ups to promote real time updates and remove blockers.
- To simplify duties, Scrum assigns distinct roles such as Product Owner and Scrum Master.
- Kanban uses a shared board to provide visual work tracking.
Predictable Delivery
One of the biggest challenges is delivering software on schedule and within budget. In order to address this, software methods include procedures that encourage predictability. With regular iterations, teams can better estimate delivery dates and manage expectations.
Predictable delivery means:
- Incremental releases rather than one big, risky launch
- Better planning of resource allocation and team availability
- Timely updates for stakeholders or users
Better Risk Management
No project is without risk, whether it’s unclear requirements or technical limitations. Software development methodologies include built in risk management mechanisms by encouraging early testing and phase based validation. Some risk reduction practices include:
- Regular sprint reviews to identify issues before they escalate
- Frequent integrations and testing cycles to catch bugs early
- Clear sign off stages before moving to the next development phase
Higher Product Quality
Quality is an outcome of methodical procedures rather than only the output of clever developers. Additionally, the majority of approaches use quality assurance procedures like feedback loops and code reviews. Additionally, these checkpoints are incorporated into the process to guarantee that the program not only functions but also satisfies usability and performance requirements. Here’s how developers ensure quality:
- Agile includes test driven development and continuous integration
- Scrum uses sprint reviews and retrospectives to fine tune deliverables
- Waterfall ensures that requirements and designs are vetted before development begins
Easier Performance Tracking
Development approaches come with built in tools for monitoring team members’ performance and keeping them accountable. Also, by defining explicit duties, such as developers owning certain tasks or Scrum Masters facilitating team health, everyone knows what’s expected of them.
Additionally, performance can be measured through:
- Burndown charts and sprint velocity
- Task boards and work-in-progress limits
- Milestone tracking and requirement checklists
Continuous Improvement Through Feedback Loops
Modern approaches are distinguished by their emphasis on ongoing improvement. Additionally, teams may consider what worked and how to do better in the future by doing retrospective and sprint reviews.
These feedback loops prevent:
- incremental enhancements to the process and the final product
- A culture of learning that promotes creativity and experimenting
- Reduced technical debt by addressing problems early
10 Top Software Development Methodologies
Agile Software Development
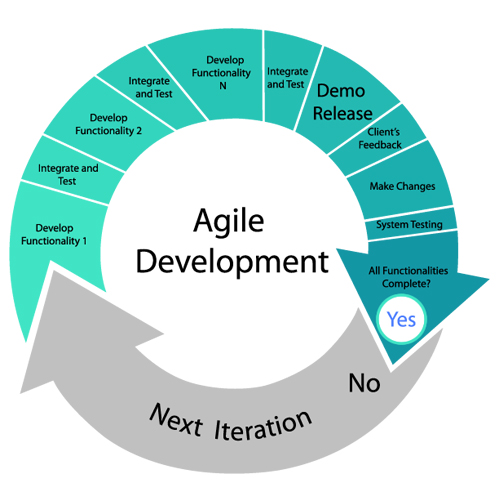
Agile is one of the most popular and transformative custom software development methodologies. Moreover, it’s centered on iterative development, where requirements and solutions change through close collaboration between cross functional teams. Furthermore, agile breaks the project into manageable sprints. These are short and fixed length iterations that result in a working product increment.
Some principles of agile include:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
- Working software delivered frequently
Teams can swiftly adapt to changes in the market or customer input thanks to agile. It’s perfect for projects where speed and creativity are essential or if the final objective isn’t entirely clear up front.
Pros
- Promotes fast delivery and adaptability to change
- Encourages ongoing customer feedback
- Improves product quality through continuous testing
- High team collaboration and transparency
Cons
- Requires experienced team members for effective execution
- Encourages ongoing customer feedback
- Improves product quality through continuous testing
- High team collaboration and transparency
Waterfall Development
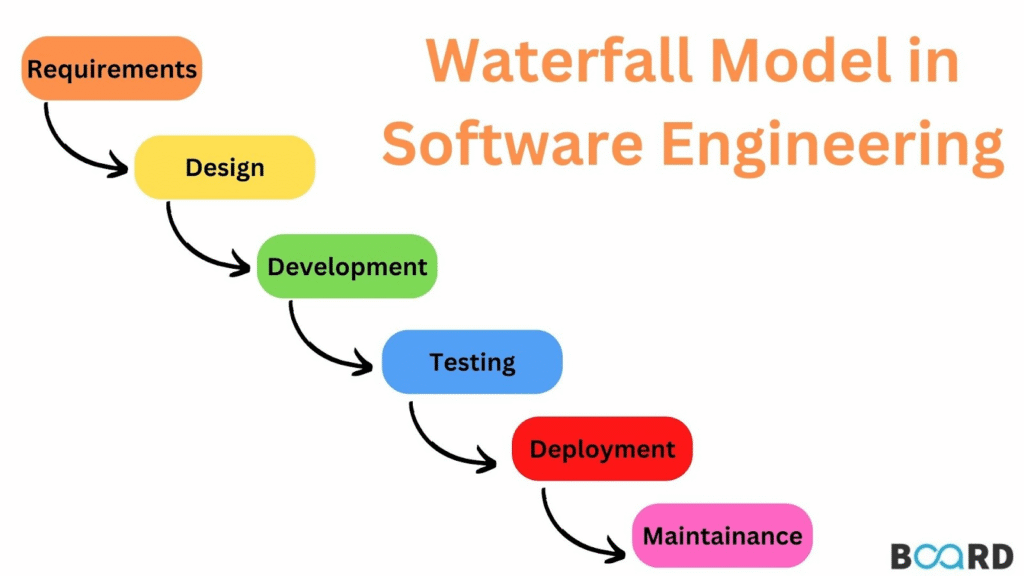
Waterfall is a traditional linear and sequential development methodology. Additionally, it employs a methodical process in which every stage—from requirements collection to maintenance—must be finished before going on to the next.
Additionally, it works best on projects with clear needs and minimal anticipated change. As a result, Waterfall offers extensive documentation and a well defined process from beginning to end.
Pros
- Simple to understand and manage
- Clearly defined stages and milestones
- Well documented process with clear deliverables
- Ideal for fixed scope and fixed budget projects
Cons
- Inflexible to changing requirements
- Late discovery of issues due to limited customer involvement
- Poor adaptability in complex or iterative projects
Lean Development
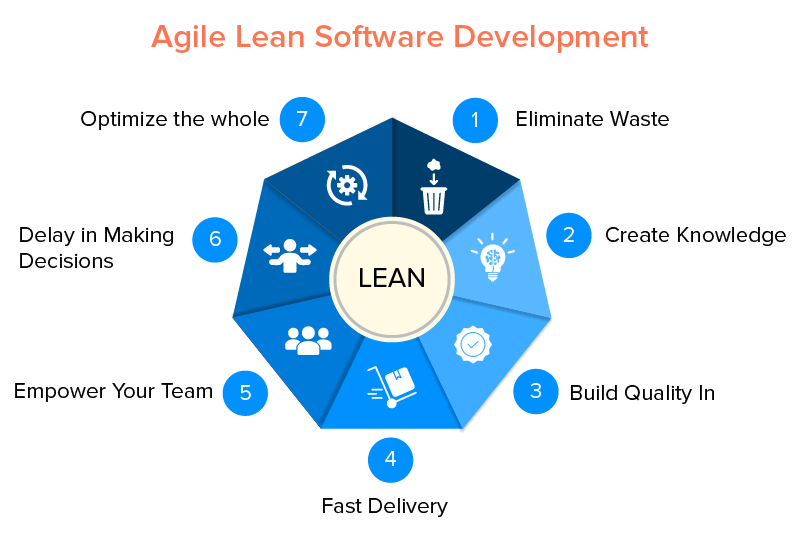
Efficiency optimization and speedy customer value delivery are the main goals of lean development. Additionally, it encourages empowered teams and eliminates everything that doesn’t improve the final result.
Additionally, companies and organizations that want to quickly deliver minimal viable products and learn from customer input will find that lean development is very helpful.
Pros
- Fast and efficient workflow
- Reduces unnecessary work and costs
- Empowers teams to take ownership
- Encourages innovation and continuous improvement
Cons
- It can be challenging to scale in large teams
- Requires a high level of discipline and commitment
- Misunderstood implementation can lead to skipping
Scrum Development
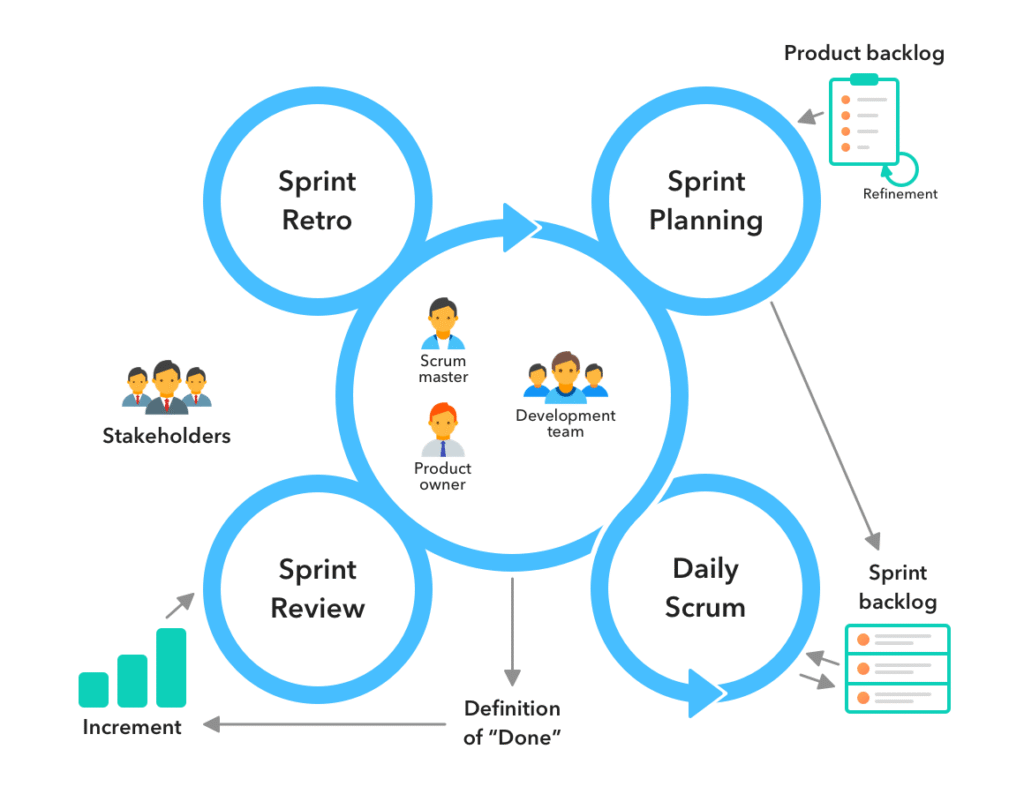
Perhaps the most popular Agile framework is Scrum, which is a subset of Agile. It also divides work into sprints of a certain length, usually two to four weeks. To track progress, the team often does stand up meetings.
Furthermore, roles such as Scrum Master are clearly defined. This ensures accountability throughout the development cycle.
Pros
- Short sprints allow for regular progress tracking
- Strong team collaboration and role clarity
- Continuous feedback and adaptation
- Encourages accountability and ownership
Cons
- Scrum requires full team commitment
- Scope changes during sprints can be disruptive
- Misunderstanding roles can derail productivity
Prototype Development
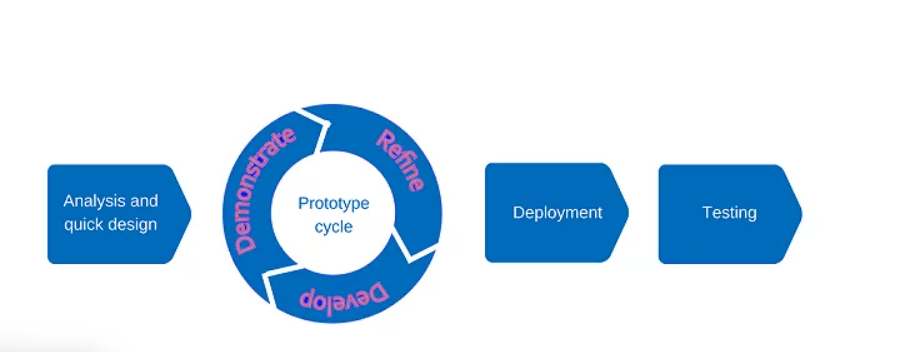
Creating working prototypes at the very beginning of a project is the aim of prototype development. Additionally, these prototypes enable stakeholders and users to provide early input and begin adjustments by providing a tangible depiction of the program.
Because the prototype helps specify user demands prior to the start of real development, this methodology is perfect when requirements are not clearly defined.
Pros
- Early detection of issues and gaps
- Improves communication with stakeholders
- Encourages user involvement from the start
- Reduces the risk of building the wrong product
Cons
- Can lead to scope creep if not controlled
- Increased development time if too many prototypes are created
- Users may mistake prototypes for the final product
Rapid Application Development
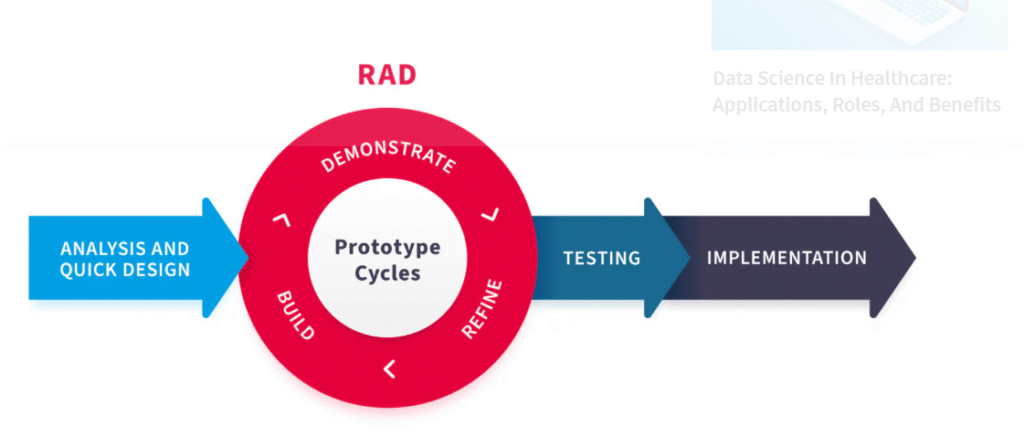
RAD prioritizes rapid prototyping over lengthy development methods. Additionally, it incorporates user participation throughout the iterative development process, which facilitates adaptation.
Moreover, RAD works well for projects with a short timeline. Also, it is also used when it is anticipated that the needs of the business will change over time.
Pros
- Faster development and delivery
- High customer involvement ensures satisfaction
- Easy to incorporate changes mid project
- Reduces overall project risk
Cons
- Not ideal for large scale or complex systems
- Requires highly skilled developers and designers
- User feedback delays can bottleneck progress
Feature Driven Development
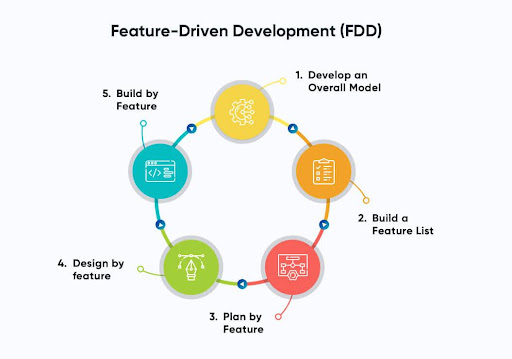
Feature driven development is a client centric Agile method that revolves around building features. Moreover, the process starts by establishing an overall model and then creating a list of features that are delivered in short and structured iterations.
Each feature is broken down into small parts and developed separately by the responsible team members. Hence, this makes it efficient for large and complex projects.
Pros
- Structured yet scalable for large teams
- Delivers tangible results frequently
- Encourages accountability with individual feature ownership
- Focuses on client valued functionality
Cons
- Less flexible compared to other Agile methods
- Requires significant upfront planning and modeling
- Can become documentation heavy
Dynamic Systems Methodology
Dynamic Systems Development is another Agile-based approach that emphasizes active user involvement and frequent delivery of products. Moreover, it follows a fixed time and resources model, adjusting features to fit within constraints rather than stretching budgets or timelines.
Additionally, this model uses iterative development and integrates practices like prioritization to manage requirements effectively.
Pros
- Time boxed iterations improve predictability
- Strong focus on stakeholder collaboration
- Clear prioritization of features
- Well documented methodology with best practices
Cons
- Requires significant user commitment
- It can be complex to implement for small teams
- Not ideal for projects with unclear goals
Rational Unified Process
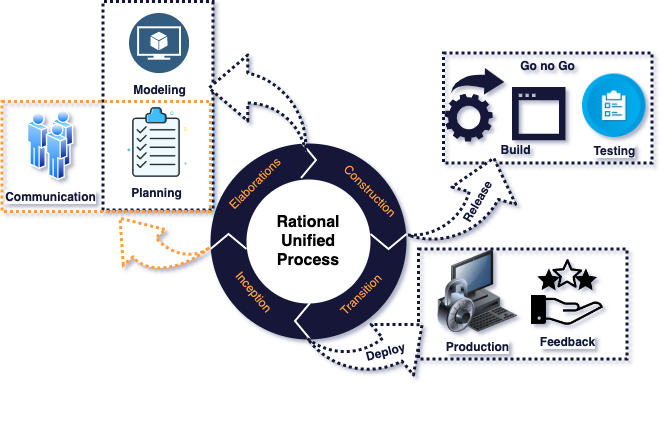
RUP is a framework developed by IBM that provides a structured approach to software development. It also separates the project into four stages. A well organized and disciplined development cycle is ensured by the defined deliverables and milestones included in each step.
Additionally, RUP incorporates aspects of both linear and iterative development. It is a hybrid technique as a result.
Pros
- Highly customizable to suit different project needs
- Emphasizes documentation and risk management
- Encourages iterative development with structured phases
- Supports large and complex systems
Cons
- Implementation can be resource intensive
- Can lead to process overhead if not tailored correctly
- Requires significant training and guidance
Adaptive Software Development
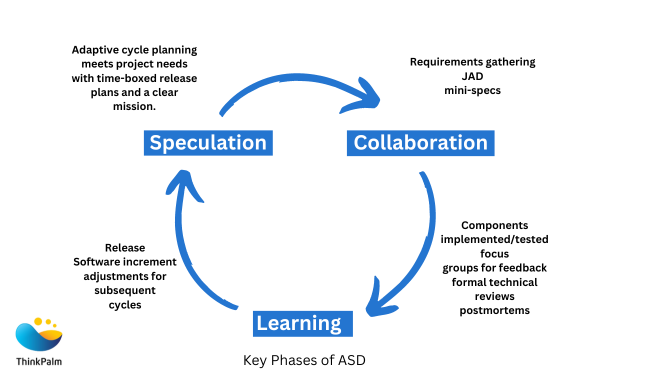
A technique called adaptive software development was created to allow for quick and adaptable development in unpredictable situations. It also emphasizes collaboration and constant flexibility. The development cycle in ASD includes three phases:
- Speculate
- Collaborate
- Learn
Furthermore, ASD is well suited for projects where innovation and experimentation are key, like research driven products.
Pros
- Promotes flexibility and innovation
- Encourages collaborative team culture
- Responds well to changing user needs
- Minimizes risks through adaptive planning
Cons
- It can lack structure if not managed properly
- Hard to track progress with loosely defined goals
- Requires high team maturity and communication
Final Words
The software development method you employ has an impact on the project’s success. There are benefits and drawbacks to every approach. This includes the flexibility of Agile and the structure of Waterfall. Therefore, teams may improve product quality and provide the groundwork for long term software delivery by matching techniques with business objectives.




