Over the next five years, Statista projects that the market for AI in cybersecurity will reach $134 billion. The rise in cybersecurity assaults is the cause of this. The frequency of cyberattacks is rising. Businesses are increasingly at risk from ransomware assaults. Traditional cybersecurity systems sometimes operate in a reactionary manner. This delay might have serious negative effects on organizations.
In this case, cybersecurity AI can be helpful. AI brings predictive capability to cybersecurity. This aids companies in anticipating issues before they arise.
In this article, we’ll discuss the critical role AI plays in cybersecurity as well as its greatest applications.
AI in Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, artificial intelligence refers to the use of data analytics and machine learning to identify and address possible cyberthreats. AI systems continually learn from data and spot abnormalities that human analysts would overlook, in contrast to conventional systems that depend on pre defined rules.
AI’s ability to assess massive datasets in real time is one of its benefits. Additionally, security experts can intervene before damage is done by spotting irregularities in normal operations. For instance, AI could see minute signs of infection long before they affect important systems.
AI also automates time consuming tasks like threat classification. This allows security professionals to focus on strategic decision making.
How AI Identifies Threats Before They Strike?

Behavioral Analysis
AI cybersecurity systems begin by learning what constitutes normal behavior within an organization’s digital ecosystem. To establish a behavioral baseline, they keep an eye on regular user activity and network traffic.
AI can quickly identify changes that point to questionable conduct after this baseline has been established. When someone suddenly logs in from an odd location or accesses personal information after work hours, for instance, the AI system detects an abnormality.
The model improves its comprehension of what normal looks like over time. This entails reducing false positives and guaranteeing precise, instantaneous detection. This behavioral approach is particularly effective against insider threats and credential based attacks.
Anomaly Detection
Machine learning algorithms are trained on massive datasets containing malicious activities. These models analyze traffic patterns and file behaviors to recognize subtle irregularities.
For instance, AI may identify anomalous file actions rather than comparing signatures to identify a malware infection.
AI is therefore especially good at spotting zero day attacks, in which malevolent actors take advantage of unknown flaws. AI guarantees defense against hitherto undiscovered dangers by spotting behavioral abnormalities instead of depending on recognized attack signatures.
Network Traffic Analysis
In order to spot questionable interactions between servers or devices, AI systems continuously scan network traffic. To identify trends like illegal access attempts or data exfiltration, they examine packet level data.
AI may immediately cut off a connection or notify administrators when it finds anomalies, such as data being transmitted to a disorganized IP address or strange surges in traffic. This level of automation greatly accelerates response times. It also prevents breaches before sensitive data leaves the network.
Furthermore, supervised and unsupervised learning models are used by AI enhanced intrusion detection systems to detect intrusions in real time. This guarantees that no harmful behavior is overlooked.
Threat Intelligence
AI doesn’t just monitor internal systems; it also gathers and analyzes global threat intelligence. Using Natural Language Process, AI can scan millions of sources and malware databases to identify emerging threats.
AI can predict possible attack vectors or campaigns aimed at the company by comparing this external data with internal network activity. Because of these predictive capabilities, security teams may apply updates or block high risk IPs before an attack even begins.
For example, AI may proactively scan an organization’s systems for associated weaknesses and start preventive actions if it discovers buzz about a new ransomware strain targeting financial organizations.
Automated Threat Hunting
Skilled analysts must manually look for Indicators of Compromise in traditional threat hunting. AI makes this procedure quicker and more effective. AI systems are also constantly searching records for subtle signs of infiltration.
AI may automatically remove access credentials or quarantine impacted devices when it detects suspicious activity. Consequently, this proactive method transforms cybersecurity into autonomous threat mitigation.
Continous Learning
Cyberthreats are dynamic. AI systems are excellent at ongoing learning. This improves their models with each new set of data or verified assault. Because of their adaptability, defenses are guaranteed to get stronger over time.
For instance, an AI model can learn particular linguistic patterns and link structures connected to a phishing campaign after it has been identified. Future attempts using similar tactics can then be blocked instantly.
What Technologies are Powering AI Cybersecurity?
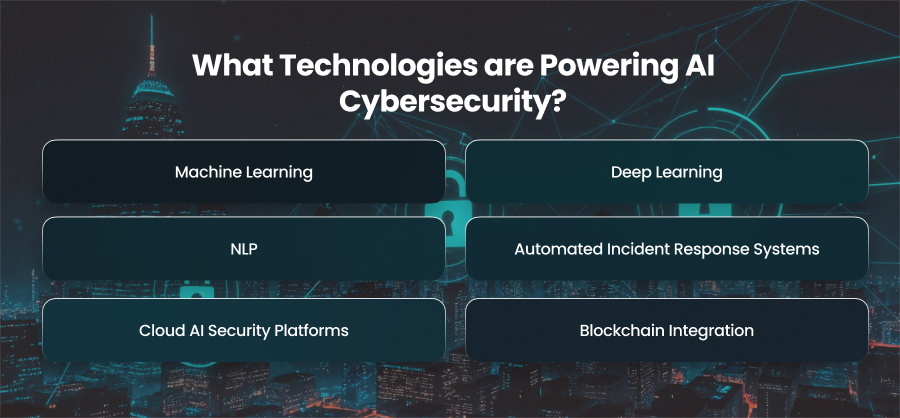
Machine Learning
Machine learning is the foundation of AI powered cybersecurity. It enables systems to recognize trends and draw lessons from historical data. Therefore, by analyzing big datasets, machine learning algorithms can distinguish between typical and abnormal behavior. These systems could get better over time and adjust to new kinds of attacks without needing to be expressly reprogrammed. Because of their capacity for dynamic learning, security systems are able to adjust to emerging threats.
Deep Learning
By using neural networks to analyze big and complicated information more efficiently, deep learning advances machine learning. It’s especially powerful in identifying hidden relationships that traditional algorithms might miss.
In cybersecurity, deep learning models are used for image recognition in malware analysis and real time monitoring of network logs. They can also identify subtle indicators of infiltration, such as phishing URLs that are camouflaged or slight changes in login patterns.
NLP
Cybersecurity systems can comprehend and assess human discourse thanks to natural language processing. This is essential for keeping an eye on communication channels and social media. Additionally, by examining linguistic indicators and contextual meaning, NLP may detect any phishing attempts or harmful intent in emails. Additionally, security analytics solutions employ it to sort through massive amounts of unstructured text data and produce insights that may be put to use.
Automated Incident Response Systems
When a danger is identified, automated incident response systems may respond quickly. They isolate compromised systems or quarantine dangerous files without requiring human intervention. These solutions limit the harm caused by cyberattacks and significantly shorten reaction times. Additionally, automation frees up security personnel to focus on complex investigations even when common risks are managed separately.
Cloud AI Security Platforms
These platforms aggregate data from multiple sources to detect patterns across vast infrastructures. They use AI to perform continuous threat hunting and security orchestration. Through shared threat data, cloud-based organizations may get insights from global cyber events to strengthen their local defenses.
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain and AI cybersecurity are being combined more and more to guarantee data openness and integrity. Blockchain makes it virtually hard for hackers to change data covertly since it saves data in decentralized, impenetrable ledgers. Blockchain data may be used by AI algorithms to authenticate transactions and safeguard IoT device interactions. Blockchain, together with AI, provides an extra degree of security. This is particularly true for sectors like banking that handle sensitive data.
Benefits of Using AI in Cybersecurity

Early Threat Detection
One of the most significant advantages of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to detect threats early. AI systems continuously analyze massive amounts of data in real time and system activities for unusual patterns. Unauthorized access attempts and data exfiltration operations are examples of signs of infiltration that machine learning models trained on past attack data may promptly detect. Organizations are able to stop threats before they become serious breaches because of this early identification.
Monitoring
Cyberattacks can occur at any time, and even a short delay in responding might have catastrophic consequences. AI enables real time monitoring of digital environments and automates responses to threats. AI can immediately ban suspect IP addresses and isolate compromised devices using automatic incident response systems.
In addition to minimizing possible harm, this lessens the effort for security staff, allowing them to concentrate on more complex investigations. Consistent responses are ensured by automating repetitive security tasks, particularly in large scale networks that process millions of transactions every day.
Reduced False Positives
The enormous volume of false positives is one of cybersecurity’s worst problems. False alarms from traditional security systems frequently overwhelm security operations centers. This is a waste of time and resources. AI uses machine learning models that continually learn from previous alarms and human interaction to assist in addressing this problem. Over time, AI becomes more adept at differentiating between harmless anomalies and actual threats. This ensures that the security staff focus on real dangers.
Improved Threat Intelligence
AI enhances threat intelligence by gathering and correlating vast amounts of data from different sources. AI can identify new risks by analyzing unstructured data using natural language processing. It then transforms this data into practical insights that security experts may utilize to strengthen defenses.
Enhanced Malware Detection
Malware and phishing are still two of the most prevalent and harmful types of cyberattacks. By spotting trends that people might miss, AI is excellent at spotting potential dangers. AI flags questionable emails for phishing by analyzing language clues and message context. AI algorithms examine the structure and coding signature of files to identify malware, even strains that have never been discovered before. Deep learning techniques can further analyze binary files or URLs to determine their intent, ensuring a multi layered defense against deceptive or malicious content. This intelligent filtering protects users and organizations from one of the most prevelant cyberattack methods.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Cybersecurity

Ensure Diverse Data
The data that AI systems are educated on determines how effective they are. To accurately identify threats, AI must be taught on a range of high quality datasets that include examples of both benign and malignant behavior. Incomplete data may lead to false keywords. Data collection from a variety of sources, including external security databases and network logs, is therefore essential. To maintain the objectivity of AI systems, regular dataset upgrades are required.
Integrate AI with Existing Security Infrastructure
Instead of operating in a vacuum, AI must seamlessly integrate with existing cybersecurity technology. This relationship enables centralized visibility and coordinated response across all security levels. By incorporating automation and predictive skills, AI may enhance conventional tools and turn them into proactive defenses.
Additionally, a well integrated system guarantees improved data flow between tools, which enhances event correlation and lowers detection delay.
Prioritize Model Tranparency
The black box aspect of certain models is one of the difficulties in applying AI for cybersecurity. This lack of openness might be dangerous in high stakes security scenarios. Explainable AI models that provide light on the reasons behind certain alerts or predictions have to be given top priority by organizations.
Continuous Learning
Cyber dangers are always evolving, and attackers are always coming up with new ways to get around protections. AI models need to be updated and retrained utilizing the most recent data in order to stay ahead. Static models may become out of date if they don’t adapt over time. Implementing continuous learning allows AI systems to adpat to emerging threats. Automated retraining pipelines can streamline processes, ensuring that models remain dynamic and responsive.
Focus on Ethical AI Use
AI must be applied ethically in cybersecurity. When creating systems, privacy regulations should be taken into account. The technology won’t inadvertently discriminate or misuse personal data thanks to ethical AI methods. Governance guidelines outlining the development of AI models should be established by organizations. Building confidence between the company and regulatory bodies is facilitated by being transparent about how data is used and obtaining user consent when needed.
Final Words
AI is changing cybersecurity by allowing intelligent automation. When used expertly with high quality data, it strengthens defenses against emerging cyberthreats. By using artificial intelligence in cybersecurity organizations can protect digital ecosystems.





