According to McKinsey & Company, 88% of companies already use AI in at least one business function, up from 78% the previous year. However, a lot of companies take an enthusiastic approach to AI but eventually fail because they attempt to automate everything without seeing where it provides value.
In this guide, we will discuss where AI helps in operations. We will also discuss where AI automation actually works and what leaders must evaluate before adopting it.
Why AI in Operations Matters?

Operations Are Becoming More Data Driven
Every operational activity produces streams of data. While this data holds immense value, most organizations are unable to process it effectively because it grows so rapidly and is often scattered across disconnected systems. AI transforms these challenges into an opportunity by analyzing massive datasets in seconds and identifying trends that humans may overlook. This shift allows operations teams to transition from reactive decision making to proactive planning.
Speed and Precision
Businesses that are unable to swiftly adjust run the danger of becoming obsolete because markets are moving more quickly than ever before. Supply chain interruptions and sudden increases in consumer demand call for quick action. Manual procedures find it difficult to offer this. AI facilitates real time decision making by automatically modifying procedures and continually monitoring operational performance. Because they can optimize operations immediately instead of waiting for evaluations, this speed provides firms a major competitive advantage.
Rising Pressure to Reduce Costs
While cost reduction has always been a major concern, modern operations need more. Businesses must find ways to reduce expenses without compromising the quality of their output. This is made possible by AI. It optimizes resource use and anticipates equipment failures before they result in downtime.
AI Reduces Human Error
Any activity carries the inherent danger of human mistake, particularly when repetitive activities require constant supervision. Errors in data input or compliance reporting might lead to costly issues and disgruntled clients. AI systems are very good at maintaining accuracy because they constantly finish jobs without becoming fatigued or sidetracked. From identifying machine anomalies to identifying patterns in financial data, artificial intelligence increases operational dependability by reducing the likelihood of errors. This increased precision aids businesses in upholding quality and fostering more consumer confidence.
Operational Areas Where AI Automation Actually Works
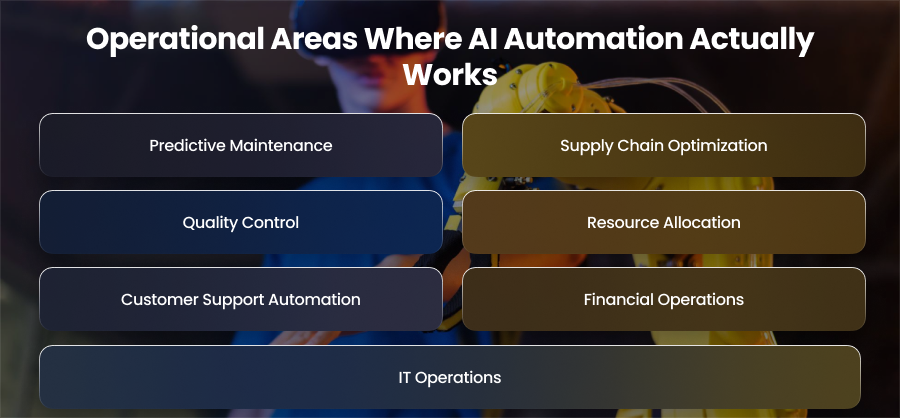
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the most successful applications of AI in operational settings. This is especially important in industries that rely on machinery. AI algorithms may examine real time sensor data to identify early indicators of failure rather than waiting for equipment to break down or adhering to set maintenance plans. This enables companies to deal with problems before they become serious ones. Less downtime is the outcome.
Supply Chain Optimization
AI has fundamentally altered how companies manage their supply networks. Traditional forecasting models often fail because they can’t account for variables that change fast. AI systems look at historical data as well as external factors like global events to better predict demand. Better inventory planning and fewer overstock scenarios follow from this.
AI also improves the efficiency of logistics by automating warehouse operations and determining the best routes for shipping. AI supply chain automation increases consumer happiness and profitability for eCommerce companies at the same time.
Quality Control
Quality control is an important but sometimes time-consuming activity in manufacturing environments. Manual inspection is prone to human mistakes and tiredness, particularly when handling large production numbers. AI improves quality control by using computer vision systems that are very accurate at identifying flaws or irregularities.
These technologies are significantly more accurate than human inspectors in identifying problems after analyzing thousands of product photos in real time. This automation is widely used in electronics manufacturing and food production.
Resource Allocation
Employee availability makes managing scheduling a challenging operational responsibility. AI analyzes past data and business requirements to automate this procedure. It can determine peak hours and allocate the appropriate number of workers with the appropriate skills at the appropriate times.
This reduces staffing issues and increases employee satisfaction by offering predictable schedules. Retail and healthcare are two sectors that greatly benefit from AI scheduling.
Customer Support Automation
Customer support automation involve large volumes of repetitive queries related to account issues and troubleshooting. By rapidly answering frequently asked inquiries, AI chatbots and virtual assistants automate the first level of service. Human agents can now handle more complicated instances as a result. These systems can understand customer intent and provide step by step solutions with high accuracy.
AI also helps support staff with sentiment analysis and automatic ticket classification. This improves the general customer experience and expedites response times.
Financial Operations
Financial operations rely heavily on data accuracy and pattern recognition. These are areas where AI performs exceptionally well. AI automates tasks such as invoice processing and financial processing. Additionally, it can identify abnormalities and analyze transactions in real time.
By continuously comparing transactions to industry standards, AI improves compliance in highly regulated industries like banking. This guarantees prompt reporting and lowers the possibility of human mistake. Additionally, by doing away with manual data entry and cross checking, it speeds up financial procedures and improves operational efficiency.
IT Operations
IT environments have grown more complicated as companies depend more and more on digital infrastructure. It is no longer possible to monitor cloud platforms and networks. IT problem solving and monitoring are automated by AIOps. AI systems constantly examine records and events to find irregularities before they affect users. They can automatically correlate alerts and suggest or execute corrective actions.
Where AI Automation Often Fails?
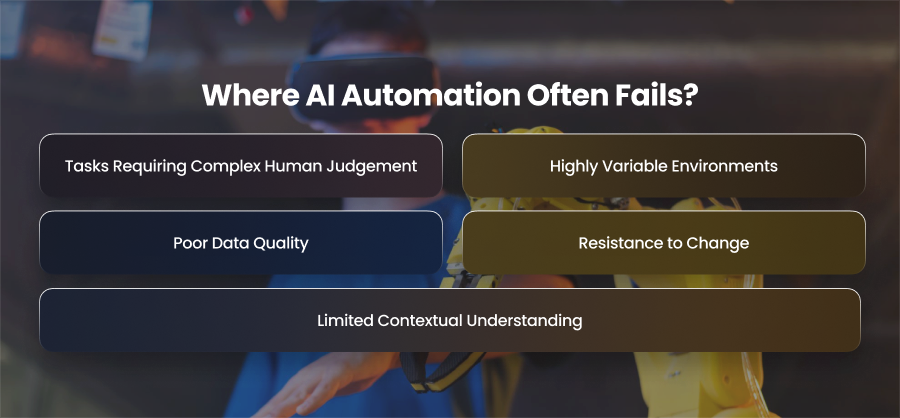
Tasks Requiring Complex Human Judgement
AI is very good at doing repeated jobs and analyzing patterns. It cannot, however, match the subtlety and discernment that people bring to difficult decision-making. AI is frequently unable to do tasks that call either originality or contextual awareness. For instance, human understanding is needed when resolving delicate consumer complaints or making important corporate choices. AI may provide recommendations or data analysis, but final decisions is such cases still rely on human judgements.
Highly Variable Environments
AI struggles when operating in environments that are unpredictable or constantly changing. Unlike controlled factory floors or structured office workflows, some operational settings are inherently consistent. Certain service positions and field activities frequently include special circumstances that are unpredictable. Automated systems struggle when faced with variety, yet they can manage repetitive jobs under standardized settings.
Poor Data Quality
One of the most frequent causes of AI initiative failure is poor data quality. Unreliable preconditions and inefficient automation result from inconsistent or incomplete data. Fragmented systems, in which vital operational data is divided among departments like finance and IT, are another issue that many businesses deal with. Furthermore, without access to correct and integrated data, AI is unable to generate significant insights.
Resistance to Change
AI adoption often fails because of human factors rather than technical limitations. Because they don’t trust AI’s judgment, workers may be against automation. Even extremely strong AI technology may perform badly if employees are unsure of how to use it. For AI to be used correctly, training is therefore necessary.
Limited Contextual Understanding
AI frequently struggles with tasks requiring a strong comprehension of context or situational nuances. AI may, for instance, recommend changes to inventories based on past patterns. However, it could not take into consideration a sudden disruption in the supply chain or an unforeseen change in the market. Similar to this, AI could misread cultural eccentricities even if it might suggest customer service activities based on sentiment analysis.
What Factors Leaders Must Evaluate Before Implementing AI?

Operational Pain Points
Whether AI is solving a genuine operational problem is the first thing executives need to evaluate. All too frequently, businesses employ AI merely for its popularity rather than because it meets a pressing need. Workflows should be mapped by leaders to identify areas where manual labor causes inefficiencies or slows down operations. Clear use cases are defined with the aid of these insights. When AI is directly applied to a clearly defined operational requirement, it provides the most benefit.
Data Availability
AI is only as powerful as the data it makes use of. Leaders must ascertain whether their company has the necessary data before implementing AI. Many companies discover their data is either missing or scattered across antiquated systems too late. AI is useless in such circumstances. Therefore, establishing data governance frameworks and ensuring reliable data pipelines are essential preconditions.
Existing Processes
It is a certain way to fail to apply AI on top of inefficient or inconsistent procedures. AI will only make these problems worse if workflows are excessively complex. Before adding automation, leaders must assess how mature their current operations are. Redesigning workflows or removing pointless stages might be part of this.
Integration Requirements
AI systems depend on reliable infrastructure. Leaders should carefully consider whether AI tools can be supported by their present technological stack. This involves assessing integration with current software and cloud readiness. Strong API support and ongoing monitoring tools are necessary for many AI applications. Before using AI, companies without these elements must think about upgrades or cloud adoption.
Security Considerations
AI introduces new data flows and sometimes external dependencies. Leaders should assess how AI technologies work and if these procedures adhere to industry rules. Sensitive data has to be shielded from abuse or breaches. In regulated businesses, this assessment is particularly important.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Operations

Start With A Defined Use Case
Businesses start with the technology rather than the issue, which is why many AI efforts fail. Identifying measurable pain areas that actually benefit from automation should be the first step for leaders. AI initiatives are guided by well defined use cases, which also guarantee congruence with corporate objectives.
Standardize Processes Before Automating
AI thrives on consistency. If the underlying workflow is inconsistent, AI will struggle to produce reliable outcomes. So, before introducing automation, organizations should map the current process and standardize steps where possible. This not only improves the baseline process but also ensures AI models have a stable foundation.
Start With a Pilot Project
The optimal strategy is to start small and expand gradually rather than trying a full-scale AI revolution right now. Teams can verify model correctness and test hypotheses through pilot projects. A successfully executed pilot also builds internal confidence and provides tangible proof that AI can deliver value.
Involve Operational Teams Early
AI adoption should never be treated ad an IT only initiative. The people who understand the process must be involved from the beginning. Their input helps refine use cases and ensure practical implementation. Furthermore, involving them early also reduces resistance to change.
Choose the Right Tech Stack
Some apps offer extensive automation features, while others specialize at specific tasks like predictive analytics or natural language processing. Based on integration capabilities and operational requirements, leaders should choose their tools.
Final Words
When used wisely and in line with actual business demands, AI in operations provides significant value. Therefore, companies may save expenses and create more robust operational procedures by carefully selecting the appropriate use cases and scaling.