According to statistics, the adoption rate of Kubernetes has significantly increased, with over 60% of enterprises now utilizing it. This is also true for companies building AI solutions. This is because models are becoming larger and data pipelines are more complex.
This is where Kubernetes can help. Once known mainly as a container orchestration tool, Kubernetes has changed into the backbone of enterprise AI systems. Moreover, it has quickly become the default platform for training models and deploying ML services.
In this guide, we’ll discuss why Kubernetes has become the standard for AI and MLOps, and how it supports the full machine learning lifecycle.
Kubernetes
An open source technology called Kubernetes was created to facilitate containerized application deployment and administration. It can handle the massive workloads running across its data centers and later donated to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation. Since then, it has become the most widely adopted orchestration tool.
At its core, Kubernetes:
- Automates the placement and scheduling of workloads
- Manages resources across clusters
- Scales applications horizontally and vertically
- Provides self healing mechanisms
- Ensures consistent environments across different machines
- Offers extensibility through operators and custom resources
Kubernetes removes the need for human server administration by enabling teams to declare their desired state, which the technology ensures is maintained.
Moreover, it’s the combination of automated orchestration and support for GPUs and specialized hardware. It also has a thriving ecosystem of ML native tools built around the platform.
Why Kubernetes Is Now the Default Platform for AI and MLOps?
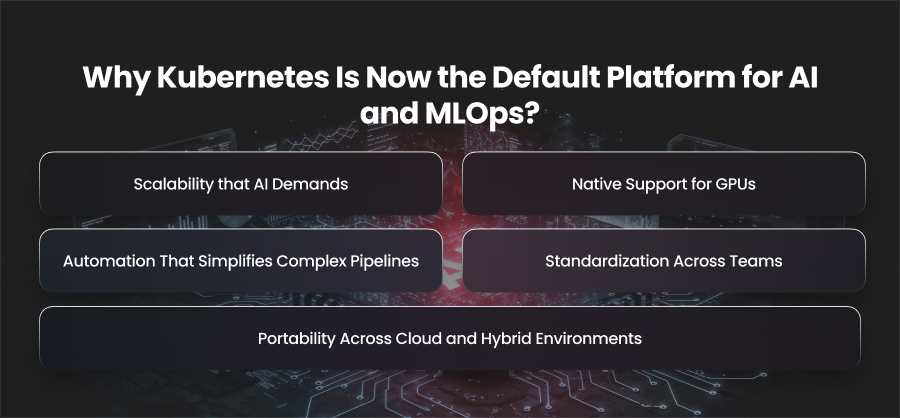
Scalability that AI Demands
AI models are growing exponentially in size. Large language models and deep learning networks need distributed training over several nodes. By dynamically starting or stopping containerized workloads in response to demand, Kubernetes facilitates horizontal scaling.
For instance, without having to manually supply servers, a data science team training an LLM may readily grow from a single GPU pod to dozens of GPU nodes. Scheduling and resource distribution among these nodes are managed by Kubernetes. This guarantees effective use and quicker model training.
For real-time inference, when the volume of queries might vary significantly, this scalability is especially essential. Additionally, inference endpoints are guaranteed to retain performance while maximizing resource utilization thanks to Kubernetes horizontal pod autoscaling.
Native Support for GPUs
GPUs and other accelerators play a major role in AI tasks. It can be difficult to manage these devices at scale, particularly when several teams want access to the same gear. This is addressed with Kubernetes’ native support for accelerators via device plugins.
- Dynamic scheduling: Kubernetes can schedule pods based on GPU availability and ensure optimal allocation.
- Multi tenant sharing: Different ML teams can share GPUs without conflict.
- Hardware abstraction: Kubernetes guarantees that containers receive the resources they require, saving developers from having to oversee low level drivers or infrastructure.
This flexibility allows organizations to scale AI workloads cost effectively while utilizing specialized hardware efficiently. It also simplifies migrating workloads between cloud providers or on premises clusters without hardware reconfiguration.
Portability Across Cloud and Hybrid Environments
AI developers frequently work in hybrid setups, with cloud based inference services and on site training clusters. Additionally, Kubernetes offers a uniform layer that hides the underlying infrastructure.
This portability ensures that:
- Models trained on one environment can run unchanged in another.
- Teams avoid vendor lock in, maintaining flexibility across AWS or on premises clusters.
- Multi cloud strategies and edge deployments become feasible without redesigning pipelines.
For companies handling sensitive data, Kubernetes makes it easier to comply with regulatory requirements by enabling hybrid deployments and isolating workloads securely.
Automation That Simplifies Complex Pipelines
Machine learning pipelines involve multiple stages. This includes data ingestion, model training, and monitoring. Kubernetes automates much of this complexity. It supports rolling updates and deployments to ensure smooth model releases, while self healing mechanisms automatically restart failed pods.
Job orchestration capabilities handle dependencies between tasks and reduce the need for manual intervention. Kubernetes also manages secrets and configuration securely. This ensures that sensitive credentials are only accessible by authorized workloads. This automation reduces operational overhead and accelerates model deployment and training.
Standardization Across Teams
Because machine learning studies must be consistent across contexts, reproducibility is essential. By running AI applications in containerized environments that incorporate all dependencies, Kubernetes promotes consistency.
Teams may collaborate and guarantee consistent model transitions from research to production by sharing prebuilt container images for experimentation. Standardized environments also simplify debugging and lower error rates, which is crucial for intricate AI pipelines with numerous interconnected parts.
How Do Kuberneters AI Agents Improve Cluster Management?
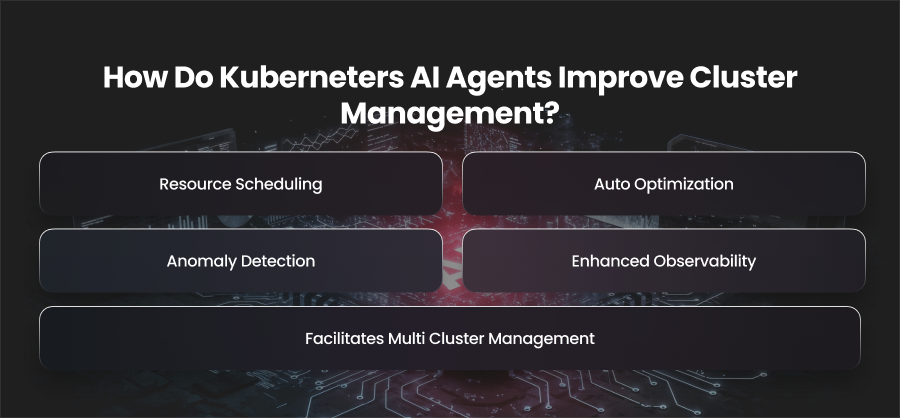
Resource Scheduling
Intelligent resource scheduling is one of the main ways Kubernetes AI agents enhance cluster management. Conventional Kubernetes scheduling depends on pre-established metrics and rules, which might not always forecast peak consumption or effectively distribute GPU and memory resources. AI agents analyze historical usage patterns and enable the clusters to scale preemptively to workloads.
For instance, the AI agent may optimize pod placement to reduce latency and increase throughput during a large scale training task, or it can assign extra GPU nodes in advance. By preventing resource contention throughout the cluster, this predictive scheduling guarantees that tasks are finished more quickly.
Auto Optimization
AI agents also enhance Kubernetes’ built in autoscaling features. While horizontal and vertical pod autoscalers react to real time metrics, AI scaling takes a proactive approach. Before the cluster’s performance deteriorates, these agents employ machine learning methods to predict workload surges and scale pods or nodes.
Additionally, by combining workloads and reallocating underutilized nodes, AI agents may maximize resource usage throughout the cluster.
Anomaly Detection
Another contribution of AI agents is intelligent anomaly detection. Unexpected failures or resource hunger can occur in Kubernetes clusters. AI agents keep an eye on indicators like network traffic and CPU use to spot trends that could point to problems.
As a result, these agents may automatically start corrective actions when abnormalities appear before the problem gets worse. As a result, this proactive self healing feature guarantees high availability and lessens the requirement for continuous human monitoring. This is particularly important for AI workloads that need ongoing training.
Enhanced Observability
Kubernetes AI agents also improve observability by providing insights beyond raw metrics. Traditional monitoring tools display CPU or pod counts, but AI agents can interpret these metrics in context and identify opportunities for optimization. They can produce actionable recommendations for cluster administrators and rebalancing workloads.
Facilitates Multi Cluster Management
For enterprises running multiple Kubernetes clusters or supporting multi cluster environments, AI agents simplify management by providing centralized intelligence. They can monitor multiple clusters simultaneously and optimize resource allocation between teams. Hence, this centralized and AI driven oversight reduces operational complexity and ensures that workloads across different teams maintain consistent performance.
Kubernetes Use Cases Across AI & ML Workloads
Large Scale Model Training
One of the most critical use cases for Kubernetes in AI is large scale distributed training. LLMs and other contemporary deep learning models demand enormous processing power distributed over several GPUs. Organizations can easily orchestrate these resources thanks to Kubernetes.
Thus, ML developers can effectively spread training workloads by utilizing operators like TFJob or Ray on Kubernetes. Thus, Kubernetes frees up data scientists to concentrate on model optimization rather than infrastructure management by automating cluster management.
Real Time Inferenace
Real time AI inference applications that need high dependability and low latency are frequently hosted on Kubernetes. Kubernetes is essential for applications like chatbots and recommendation engines to continue operating consistently even in the face of varying traffic. Organizations may implement models as scalable services with autoscaling and rollback capabilities by utilizing ML deployment frameworks such as KServe. Kubernetes ensures that inference workloads can respond to demand spikes without service disruption.
Batch Processing
Many AI pipelines involve batch processing tasks such as data processing or running inference on large datasets. Kubernetes Jobs are perfect for some workloads because they can scale elastically and reliably finish tasks at predefined intervals. For instance, a retail company may use Kubernetes to analyze millions of transactional records in order to extract features for recommendation or predictive analytics systems. Without human interaction, Kubernetes manages scheduling and makes sure batch processes finish quickly.
Multi Tenant AI Platforms
Businesses frequently have to support several ML teams using the same infrastructure. Because it offers resource limitations and namespace separation, Kubernetes performs very well in multi-tenant scenarios. Dedicated environments with restricted access to shared GPUs and networking resources are available for each team.
Several teams or business units may function autonomously while using a common AI infrastructure thanks to this strategy, which guarantees security and fairness. Centralized monitoring and governance throughout the company are made possible by multi tenant management, which also lowers operational complexity.
Edge AI
Kubernetes also supports AI workloads at the edge and real time inference close to the data source. Lightweight distributions allow organizations to deploy models on edge devices. For instance, healthcare professionals employ diagnostic models on localized devices for immediate analysis, while industrial IoT systems use Kubernetes at the edge to execute predictive maintenance models on manufacturing equipment. In federated learning systems, where models are trained across several edge devices without centralizing sensitive data, Kubernetes facilitates the management of orchestration.
AI Monitoring
Many organizations use Kubernetes to manage automated monitoring and retraining pipelines. By combining ML pipelines with Kubernetes’ autoscaling functionality, teams can build models that monitor their own performance and immediately start retraining procedures. This use case is essential for applications like recommendation engines and predictive maintenance, where models need to react fast to changing data patterns. Kubernetes minimizes downtime by ensuring that these retention channels operate dependably.
What Are the Best Practices for Deploying Kubernetes AI Agents?

Implement Strong Guardrails
To keep AI agents from acting too aggressively or making poor judgments, they should follow a defined set of rules. These safeguards can be enforced via native Kubernetes policy frameworks like OPA Gatekeeper or integrated admission controllers. For example, guardrails can prevent AI agents from scaling critical workloads below a certain threshold or running automated remediation during peak business hours.
Use Dedicated Namespaces
AI agents often require elevated access to cluster metrics and resource configurations. To maintain security and organization, it is best to deploy AI agents in dedicated namespaces and apply granular Role Based Access Control pipelines. This ensures the agent only accesses the resources it needs.
Ensure High Quality Data Feeds
AI agents rely on data to make optimal decisions. Incomplete data can lead to inaccurate predictions or false anomaly alerts. Implementing strong observability practices using Grafana ensures that AI agents receive clean and consistent inputs. Additionally, setting up long term storage for metrics and logs provides the historical context agents need for trend analysis.
Optimize Resource Allocation
AI agents often include background processing or machine learning models. To operate efficiently, they need appropriately sized compute and storage resources. Under provisioned agents can lag or provide delayed insights. Using Kubernetes resource requests, limits, and autoscaling ensures the agent runs efficiently without impacting user workloads.
Use Incremental Rollouts
Kubernetes AI agents should be rolled out gradually. Canary deployments allow teams to monitor how the agent behaves at small scales before fully enabling it across the cluster. This prevents unexpected behavior from affecting mission critical AI workloads such as distributed training.
Final Words
Due to its unparalleled scalability and dependability, Kubernetes has become essential for contemporary AI and MLOps. Organizations can execute AI workloads with confidence at any scale and optimize operations with the help of AI agents that increase optimization and self management.