In the next three years, 80% of AI data will be artificially created, predicts Gartner. This is due to the fact that AI systems are information driven. An AI model’s efficacy is largely dependent on the quality of data utilized to train it.
However, obtaining high quality data is sometimes fraught with substantial challenges. These include data shortages. In this case, synthetic data may be helpful.
Generated by algorithms, synthetic data is changing how organizations train and deploy AI models. In this guide, we will discuss how synthetic data mitigates the risk of handling information and how it can help build better AI models.
Synthetic Data
Synthetic data refers to artificially generated data that imitates the properties and patterns of real world datasets. Unlike anonymized or augmented data derived from real examples, synthetic data is created entirely from scratch using algorithms or machine learning models. The goal is to produce data that behaves like real data in statistical and structural terms while containing no actual personal or property information.
The advantage of synthetic data is control. Unlike real data, which is limited by the conditions of collection, synthetic data may be customized to fulfill specific training goals. This suggests that developers could produce more balanced datasets without sacrificing their utility.
Why Synthetic Data Matters in AI Development?

Overcoming Data Security and Imbalance
Large, well balanced datasets that capture a variety of situations are ideal for AI models. However, real world data is either hard to get or dispersed unevenly in many businesses. For example, the small number of patients in the healthcare industry might make it very hard to collect enough data on uncommon diseases. Similarly, it is not possible to gather millions of instances of uncommon accident situations for autonomous driving.
Synthetic data solves this problem by generating realistic yet diverse examples on demand. Developers can create thousands of unique edge cases. This guarantees that the model is subjected to all potential variations. Furthermore, this extensive training results in more robust AI systems that operate dependably in real world situations.
Preserving Privacy
Organizations now find it more challenging to openly communicate or use personal data due to data privacy restrictions. There are significant ethical and legal issues when even anonymised datasets may occasionally be re identified. Synthetic data provides a solution; it contains no real user information yet retains the statistical and structural characteristics of the original dataset.
This means businesses can train and share AI models without risking privacy violations. For example, a financial institution can use synthetic transaction data to develop fraud detection algorithms without exposing sensitive customer data to develop fraud detection algorithms without exposing sensitive customer details.
Reducing Time and Cost in Data Collection
Collecting and maintaining real world data is an expensive and time consuming process. In fields like computer vision, building labeled datasets can take months or even years. Synthetic data significantly cuts down this effort; it can be generated quickly and automatically with precise control over volume and quality.
Instead of waiting for real data to be gathered, organizations can simulate millions of labeled examples in a fraction of the time. For example, a retail company may take fictitious photos of products in various lighting conditions in order to train visual recognition models faster.
Enabling Safer Testing
Some real world scenarios are too costly or rare to test directly. Moreover, in fields like aviation, conducting live experiments poses significant safety risks. Synthetic data allows organizations to simulate these high risk environments virtually.
For instance, autonomous driving systems can be trained using synthetic crash simulations or unpredictable pedestrian behavior. This enables AI models to learn safely from extreme situations without consequences. Similar to this, artificial intelligence systems could be able to identify threats more accurately if they use synthetic cybersecurity data to model hundreds of possible attack scenarios.
Enhancing Data Diversity
One of the biggest challenges in AI development is data bias. When training data is AI systems can become prejudiced. This leads to unfair outcomes.
By balancing datasets and addressing data gaps, synthetic data can be quite helpful in resolving this problem. To promote a more balanced distribution of data, developers might construct situations or groups that are underrepresented. In recruitment AI tools, for instance, a variety of candidate backgrounds may be represented by synthetic data, leading to more inclusive model projections. By using synthetic data strategically, businesses may lessen discrimination.
How Synthetic Data Improves Model Accuracy and Reliability?

Simulating Rare Scenarios
One of the biggest advantages of synthetic data is its ability to generate rare or extreme cases that are almost impossible to collect in real life. For example, consider self driving car systems. These models need to be trained on countless driving situtions. Consequently, it is not only challenging but also risky to record such occurrences in the actual world.
Developers may safely and effectively mimic these uncommon situations with the use of synthetic data. Through exposure to thousands of believable but hypothetical edge cases, the model learns how to respond to unexpected situations.
Artificial intelligence systems can more accurately identify anomalies like fraudulent transactions with the use of synthetic data.
Balancing Datasets
AI bais remains one of the most pressing challenges in machine learning. The model has a tendency to anticipate minorities incorrectly and favor the majority when real world data is biased. This damages model accuracy and erodes confidence.
By producing samples from underrepresented categories, synthetic data aids in rebalancing training datasets. For example, low samples may result in poor performance of a facial recognition model on specific ethnic groups. In order to ensure that the models handle different populations equally, synthetic augmentation can provide a variety of face variants.
Similar to this, in the medical field, artificial patient data may close gaps in low-occurrence illnesses, providing diagnostic models with a more thorough grasp of disease trends. Ethical integrity is enhanced when balanced datasets are used to create models that function consistently across all user groups.
Increasing Data Volumes
Large amounts of data are crucial for AI models, especially deep learning systems, to achieve high accuracy. However, gathering and categorizing millions of real world samples is expensive. Moreover, large amounts of synthetic data may be produced. Hence, this allows developers to train models with extensive datasets that would otherwise be impossible to compile.
In addition to improving the statistical significance of the model’s learning, using extensive synthetic training data also aids in identifying minute patterns that smaller datasets would overlook. When combined with real world data, synthetic examples provide greater diversity, ensuring that the model learns more fully.
Reducing Overfitting Through Control Diversity
When an AI model performs well on training data but badly on unknown data, it is said to be overfitting; in other words, it is simply memorizing patterns rather than comprehending them. This is often caused by limited or repetitive datasets. Furthermore, by offering realistic and redundant versions of the data, synthetic data delivers controlled variety to prevent outfitting.
Synthetic data guarantees that the model learns basic principles rather than recalling particular examples by purposefully making minor adjustments to the dataset. This enhances the model’s capacity to adjust to novel settings.
Supporting Reliable Model Testing
Just as important as training an AI model is testing it. The diversity required to thoroughly assess a model’s advantages and disadvantages is frequently lacking in real world testing data. Synthetic data can help in generating controlled test scenarios with lots of input variables.
What Are the Techniques for Generating Synthetic Data?
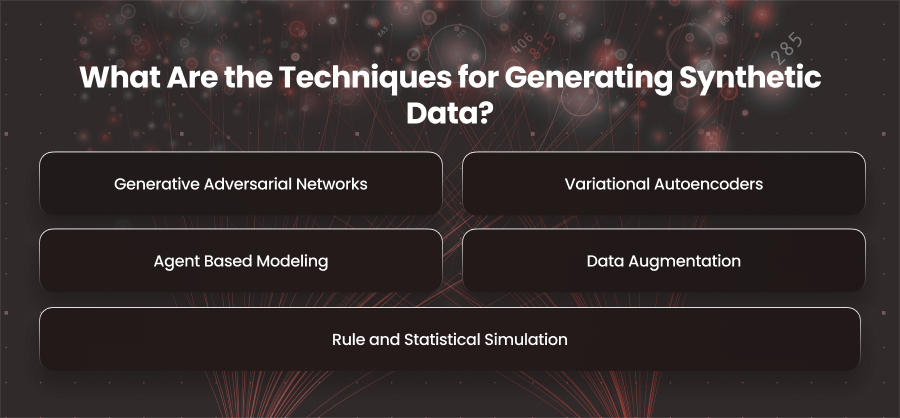
Generative Adversarial Networks
Generative Adversarial Networks are among the most effective methods for creating synthetic data. Adversarial training is the process by which two neural networks. This includes a generator and an administrator. Both of these compete with one another to form a GAN.
- In an attempt to mimic actual data, the generator generates synthetic samples.
- The discriminator assesses both synthetic and real samples to identify the authentic ones.
Overtime, the generator improves its output until the synthetic data becomes indistinguishable from the real dataset. GANs have been widely used for generating realistic images and even tabular data for training AI systems.
Variational Autoencoders
Another advanced method is variational autoencoders, a type of deep learning architecture designed for probabilistic data generation. Prior to reconstructing it into new synthetic samples, VAEs compress input data into a latent space.
Furthermore, rather than creating flawless clones, VAEs concentrate on capturing the data’s underlying dispersion. This makes them extremely beneficial for creating variable datasets, especially for training AI models that need to handle multiple edge situations.
Agent Based Modeling
Agent Based Modeling is a simulation approach used to generate synthetic data that captures interactions between multiple entities in complex environments. Each agent operates based on predefined rules. This allows researchers to observe how systems change over time.
ABM is particularly useful for traffic simulations, where the goal is to understand how individual behaviors influence collective outcomes. For example, ABM can simulate how customers interact in a retail environment.
Rule and Statistical Simulation
In some scenarios, simple rule based systems or statistical models are enough to generate high quality synthetic data. These systems rely on domain expertise and statistical distributions derived from real data.
- Rule based systems generate data based on logical conditions and constraints.
- Gaussian distributions are used in statistical simulations to replicate trends in real world datasets.
Data Augmentation
Data augmentation is one of the most accesible forms of synthetic data generation. It doesn’t create entirely new datasets but rather expands existing ones by applying transformations that simulate real world variability.
Common augmentation techniques includes:
- Rotating or flipping images in computer vision tasks
- Addding noise to audio data
- Paraphrasing text in NLP tasks
- Randomly changing values in tabular datasets
Best Practices for Using Synthetic Data Effectively

Start with a Clear Objective
Determine your needs and the issue that the synthetic data is intended to address before creating it. Therefore, setting clear objectives guarantees that your data creation procedure remains in line with the planned procedure of your model.
For instance, simulating infrequent fraudulent transactions that are underrepresented in real datasets might be the goal of an AI project if it entails training a fraud detection system. On the other hand, in order to retain realistic medical correlations and protect patient privacy, a healthcare AI system could require fake data.
Maintain Realism and Statistical Integrity
High quality synthetic data should mirror statistical characteristics and underlying distributions of real data. It’s enough to create random samples, the synthetic data must capture real world correlations and relationships between variables.
To achieve this:
- Use distribution analysis and statistical metrics to compare real and synthetic datasets.
- Monitor parameters such as mean and correlation coefficients.
Combine Real and Synthetic Data for Better Results
While synthetic data can stand alone, it often performs best when blended with real data. This hybrid approach provides the models with the authenticity of real world examples and the diversity of synthetic variations.
A balanced mix of both types of data helps:
- Enhance model generalization across edge cases.
- Prevent overfitting on limited real data.
- Ensure realistic predictions that translate well to actual use cases.
Validate Synthetic Data Thoroughly
One of the most important but often disregarded phases in the lifetime of synthetic data is validation. Synthetic datasets have the potential to introduce bias that jeopardize the integrity of the model if they are not properly validated. Confirming that the synthetic data behaves and appears like actual data during training is the aim.
Prioritize Data Privacy
One of the synthetic data’s biggest advantages is its potential to enhance privacy, but this only holds true when generation processes are designed responsibly. Even synthetic datasets can leak information if they inadvertently contain sensitive details from real world records.
Final Words
Synthetic data can address data scarcity and bias. It improves model scalability and accuracy when produced and used strategically. Organizations may use synthetic data as a strong and moral basis for developing more intelligent AI systems by adhering to best practices.




