We are living in the age of integration and today exchanging data between two or more systems is more crucial than it was ever before. For instance, the Uber app needs location access from Google Maps and also payment access from the financial apps.
The middleman between the two apps that connects them and helps them in communication is known as API or you can say Application Program Interface.
There are different ways to create an API, but two of the most common and essential ones are REST APIs and RESTful APIs. These two help in making software interactions in the projects easy.
What Is REST API?

REST API uses HTTP requests to get and use information. It is an architectural-style API that securely exchanges information over the internet. REST API is a way by which two computer systems communicate with each other.
Imagine you’re searching for something on the internet and you get results for a specific service. REST APIs work in the same way.
The set of rules that developers create on the server side that help programs to communicate, is known as API. REST controls how the API will work and look, as well as what architectural pattern developers can use to create it.
What Is RESTful API?

RESTful API allows two different systems to communicate and exchange information over the internet but under high security. This API offers a simple, easy, and adaptable way to create APIs that can be used on different platforms and programming languages.
If you want to enhance your team skills in these areas, the best choice is to Node js developers. RESTful API follows the REST architecture that allows them to be quick and adaptable and supports all types of information.
Difference Between REST API and RESTful API
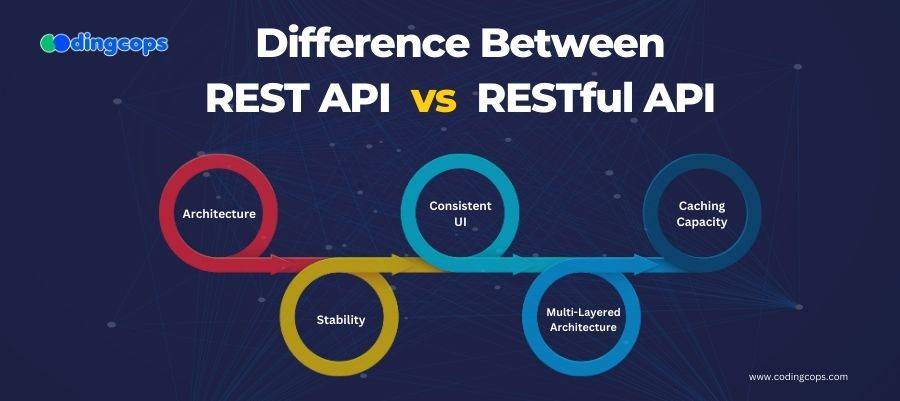
The difference between REST API and RESTful API is not obvious at first. In simple terms, there is actually no particular difference between REST and RESTful when it comes to APIs. The only difference is that both of these are used for different functions.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style and is a collection of constraints. While RESTful is a web service that uses the REST architectural style. RESTful is used in apps, software, and web services. It is the API that follows the REST constraints.
Architecture
When it comes to REST application architecture, it has a client-side with even UI and a layer system. Contrary to that, a RESTful application has the same architecture as REST but there will be some additional features.
Moreover, a REST server works with a client-server and handles user interactions. The REST framework uses an independent system to manage the performance of the application. It updates in individual tracks if there is any possibility of any update or improvement.
Caching Capacity
When it comes to REST APIs, they can suggest whether data is cacheable or non-cacheable, if there is a need to replace the non-cacheable data. On the other hand, with RESTful app clients can always use cacheable data anytime and anywhere.
With REST APIs the clients and infrastructure can store data, so you can easily improve the functionality and performance of the systems. The system can easily displace the non-cacheable data when no one is using the stored data.
Whereas, when you create a RESTful API, you easily get access to changing states and cacheable data according to your requirements. It also helps you adapt the system and follow the latest enterprise web development trends according to your needs.
Consistent UI
One of the basic and important components of REST apps is the consistent or uniform user interface. This is the most significant factor that differentiates REST from other network patterns. With REST APIs, developers can easily maintain a constant interface across multiple devices.
Both REST and RESTful systems are good at handling information as resources and they do it with unique and individual context. For businesses that want to add value to their development teams, it is beneficial to Java developers as they are experts in creating stable interfaces for complex apps.
Stability
With the REST apps, the client is dealing with each app phase and they keep up with no client state. While RESTful servers hide the implementation.
There is an exchange of information between the server and the client about data and state with REST frameworks. Whereas the RESTful web services do not hide any information.
RESTful API vs REST API
Let’s have a look at the other differentiating factors of REST and RESTful API:
- RESTful API works on REST infrastructure and apps. While REST API is based on response and request, and it uses web services.
- The information format of RESTful API depends on JSON, Text, and HTTP. While REST API depends on HTTP.
- RESTful applications consume less bandwidth, while REST apps consume only minimum bandwidth.
- When it comes to REST APIs, they are adaptable and extremely user-friendly. While RESTful APIs are too flexible as to RESTless APIs.
- REST API allows communication between the client and the server. While RESTful uses REST infrastructure and allows compatibility between different systems.
- REST API does not follow any pattern, while RESTful API follows the Model View Controller (MVC) pattern.
- REST app works on request and response and RESTful API totally depends on the REST applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between REST API and RESTful API entirely depends on the needs of your project. If you need flexibility in your project and it is a small or less complex project, a REST API can be the best choice. On the other hand, if you’re creating a larger solution or app where the focus is on adaptability and performance, then RESTful API is the ideal choice.
More Related Blogs
- React vs. Backbone.js
- Top 10 Future of React in 2024
- React Lifecycle Methods
- React State Management Libraries
- dedicated React developers
- Spring Boot Developers
Frequently Asked Questions
– GET (retrieve a resource)
– POST (create a new resource)
– PUT (update an existing resource)
– DELETE (remove a resource)
– PATCH (apply partial modifications to a resource)