Over the next three years, cybercrime is predicted to cost the world $13.82 trillion, according to Statista. Cybersecurity is becoming a critical problem rather than a minor one for businesses.
Furthermore, criminals now have more opportunities than ever to exploit weaknesses due to the growth of digital transformation. Therefore, everyone is vulnerable, regardless of the size of their company.
So, in this guide, we will look at some of the pressing cybersecurity threats that organizations face these days. Moreover, we will discuss all the best practices to mitigate these threats.
Cybersecurity Risks
Malevolent attempts by people or groups to compromise the confidentiality and integrity of digital systems are known as cybersecurity threats. These dangers might also originate from a variety of sources.
Cybersecurity risks also take advantage of flaws in network or software setups. Furthermore, cybersecurity problems have financial and legal ramifications in addition to being technological. Operational interruptions and data breaches might result from successful attacks. These attacks may potentially result in fines from the government and a decline in consumer confidence.
Threats are only going to grow as more businesses use cloud infrastructures and IoT devices. Additionally, cybercriminals are becoming more skilled and are creating and disseminating sophisticated attack tools through the use of AI and underground marketplaces.
Top Cybersecurity Risks
Phishing
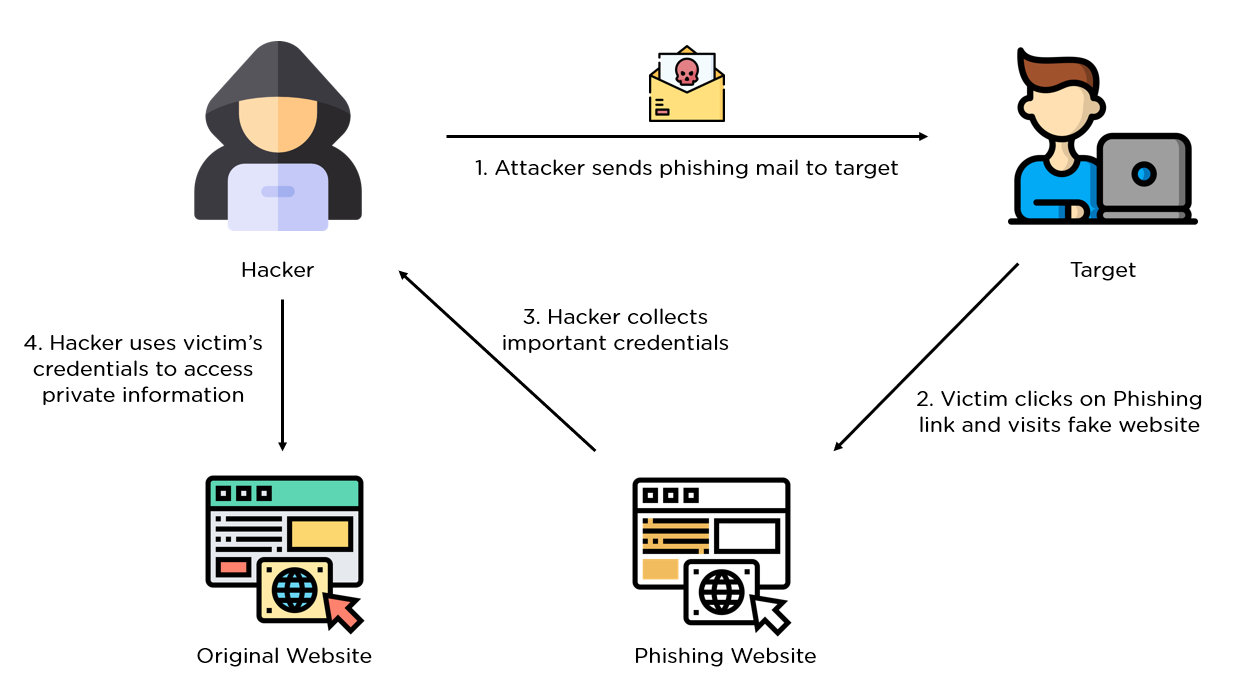
One of the most frequent cybersecurity risks that people and companies have to deal with is phishing attacks. Furthermore, in a typical phishing attack, hackers assume the identity of a reliable source, such as a bank or a coworker. They then trick the victim into divulging personal information. These consist of social security numbers or login credentials. Additionally, emails and texts are frequently used in these attacks.
More sophisticated variations, such as spear phishing and whaling, target certain people, such as IT administrators or executives. Additionally, last year saw a rise in phishing attacks that used reliable file hosting websites. This is due to the fact that social engineering and human mistakes are key components of phishing. Therefore, it remains difficult to eliminate phishing.
Ransomware
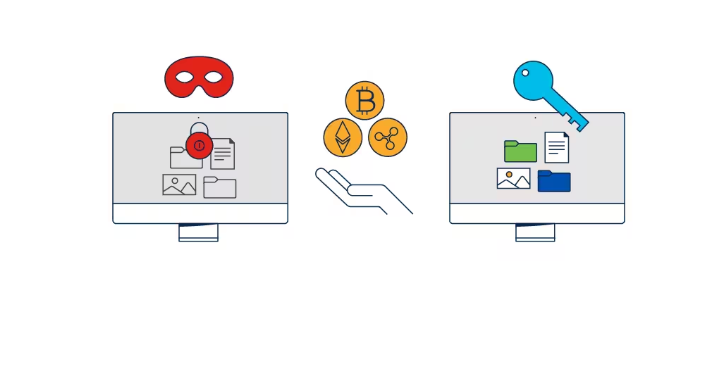
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that can encrypt files and keep you from using your computer. This is until you pay a ransom. A notice requesting payment for the decryption key is displayed to you. Furthermore, some ransomware variants use double and triple extortion tactics. This means that your data is not only encrypted but also stolen and threatened to be published or sold unless you pay the ransom.
For example, the Change Healthcare ransomware attack is the biggest breach of medical data in the US. This breach exposed sensitive data for 190 million people.
Insider Threats
The next threat is insider threats. These attacks originate within your organization. Additionally, these assaults target workers or other reliable people who have access to data and systems. Moreover, these assaults may be unintentional or deliberate. However, because insider attacks take advantage of approved access, they are riskier. To lower the danger of insider attacks, businesses need to put strict access restrictions in place and offer continuous cybersecurity training.
Cloud Security Risks
Businesses use cloud environments. They now confront a different set of difficulties, though. Despite the robust baseline security provided by cloud providers, customers frequently claim security breaches brought on by user errors, such as incorrectly configured permissions and unprotected databases. Furthermore, insecure APIs and data leakage are further issues. Furthermore, shared responsibility models mean that cloud users must ensure proper configuration and monitoring. But without robust cloud security strategies, organizations can expose themselves to severe vulnerabilities.
IoT Vulnerabilities
By linking anything from industrial control systems to smart thermostats, the Internet of Things is revolutionizing a variety of sectors. But as the number of linked devices has increased, fraudsters now have a larger attack surface. Basic security elements like appropriate authentication and encrypted communication are absent from a large number of IoT devices. So, once these devices are compromised, these devices can be used as entry points into larger networks. For example, there are reports of 6000 attacks on connected devices in the manufacturing industry per week.
Malware
Malware includes a number of threats, such as viruses and spyware. These can damage and gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Furthermore, attackers can deliver malware through infected email attachments. Moreover, they can also bundle malware with legitimate software.
Furthermore, some spyware might totally lock you out of your computer, while others quietly gather data. Additionally, the intricacy of contemporary malware, especially polymorphic forms, allows them to alter their code in order to avoid detection. Hence, this makes malware a persistent threat.
Therefore, by updating your software and using safe browsing techniques, you can protect yourself against viruses. To guarantee the security of your application, you might hire software engineers who are knowledgeable with DevSecOps methodologies.
DDoS
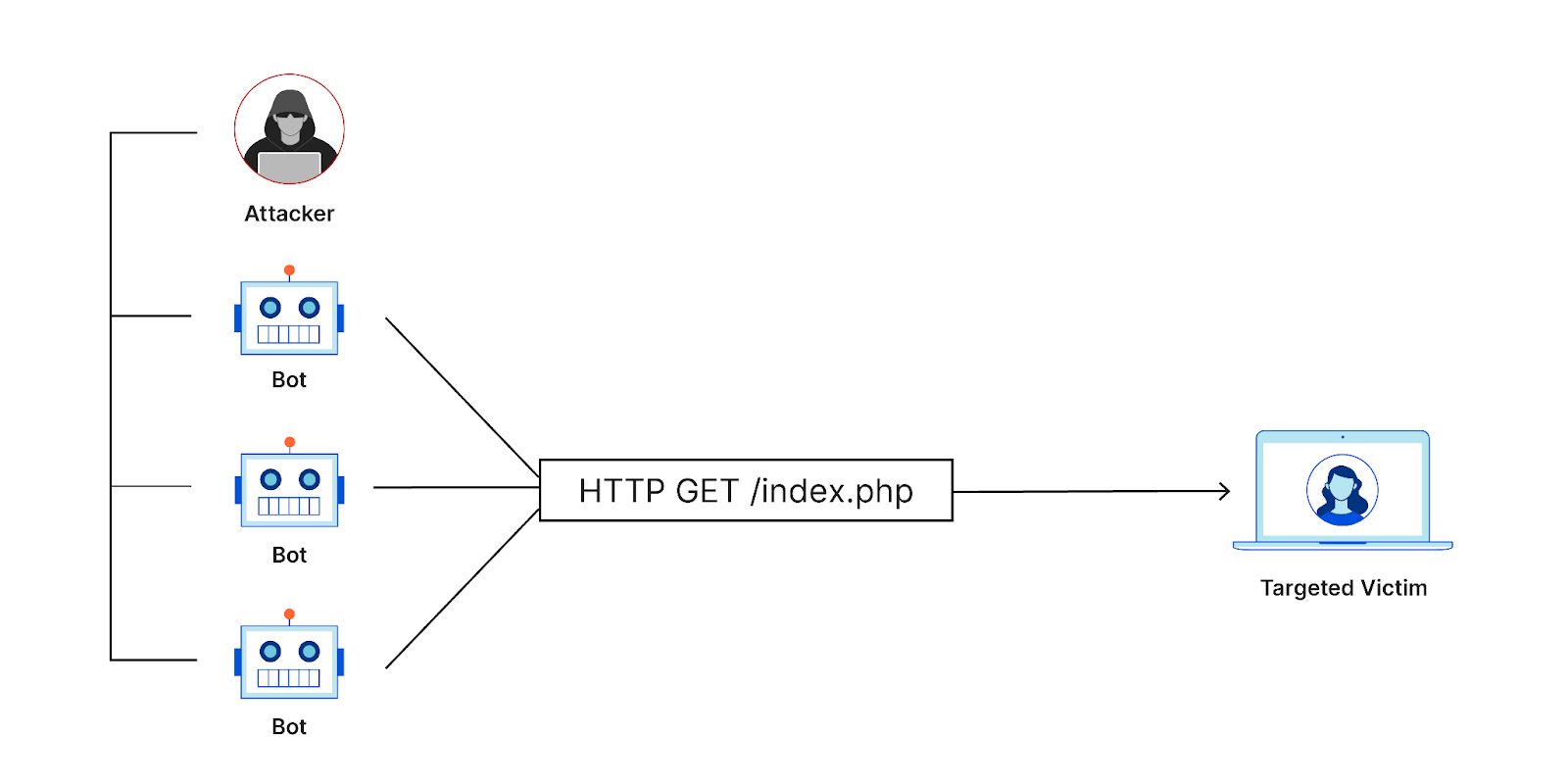
DDoS attacks can overwhelm a targeted website or server with traffic. As a result, this can stop authorized users from seeing your website. Furthermore, massive networks of hacked devices are used to conduct these assaults. These attacks can last anywhere from a few minutes to several days and cause substantial financial loss. Microsoft saw an extended outage due to a large scale DDoS attack.
These attacks also act as a smokescreen to distract IT personnel from more intricate attacks. Thus, by combining defenses like rate limitation and traffic filtering, you can lessen these threats.
Business Email Threats
Business email breach is a highly targeted cyberattack in which hackers utilize phony or stolen email accounts to trick companies into disclosing private information or funds. In order to exploit the power and trust within your company, these attackers also pose as your executives or suppliers.
Supply Chain Attacks
Attacks on the supply chain are another detrimental cybersecurity problem. In these assaults, thieves get access to your company by breaching a third-party service. Because they take advantage of dependable connections, these assaults are more risky. The SolarWinds breach, in which harmful malware was included within a software update distributed to thousands of users, including government institutions, is among the most well-known examples.
Drive-by Compromise
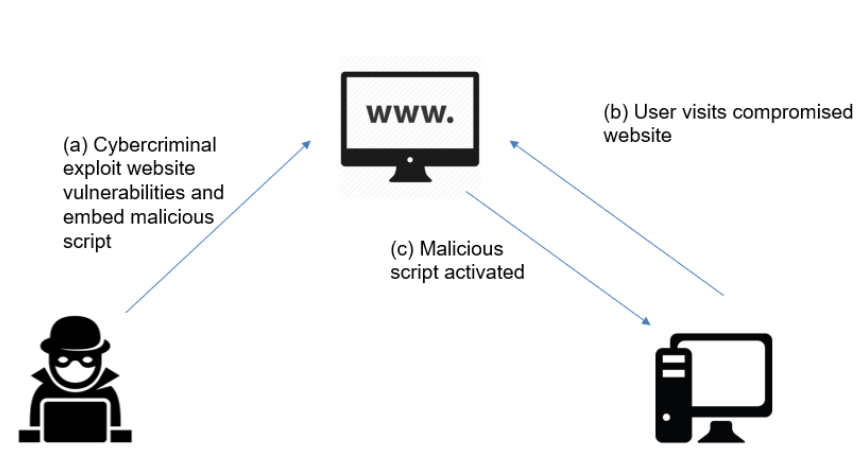
A drive by compromise happens when you visit a compromised website that automatically and silently downloads malware onto your system. Furthermore, these attacks take advantage of vulnerabilities in browsers and plugins. Moreover, since it requires no direct interaction beyond visiting a page, drive-by attacks are especially insidious.
Deepfake Technology
Deepfakes use artificial intelligence to produce incredibly lifelike but fake audio and video content. This technology presents serious cybersecurity dangers even if it has some valid applications in entertainment and education. Attackers can use this to pose as government officials or executive in order to coerce you into doing harmful things.
Defense Evasion
One strategy hackers employ to get around conventional security measures and stay hidden within a system or network is defense evasion. Attackers employ defensive evasion strategies to blend in with legal activities rather than initiating brute force attacks. As a result, detection becomes much more challenging.
Mitigating Cybersecurity Threats: Best Practices

Implement a Strong Cybersecurity Framework
You should start by implementing a cybersecurity framework such as CIS controls. Furthermore, such a framework provides thorough instructions for recognizing and preventing cyber problems. Therefore, you may guarantee systematic and prioritized risk management throughout the company by coordinating your security efforts with such frameworks.
Security Training
One of the biggest reasons for cybersecurity issues is still human mistakes. Furthermore, regular training helps employees recognize phishing emails and handle sensitive data properly. Also, this training can help employees report anomalies quickly.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Simply using usernames and passwords, multi-factor authentication offers an additional degree of security. An attacker would still require the second form of verification even if your credentials were stolen. This verification includes the mobile app code or hardware token. Thus, multi factor authentication is especially important for accessing email and cloud applications.
Software Upgradation

Software that is outdated is frequently exploited. Therefore, it is important to apply patches as quickly as possible to help address known vulnerabilities in operating systems and firmware. Furthermore, automated patch management systems help expedite the process while ensuring that no crucial updates are overlooked.
Least Privilege
Not every worker needs access to every file or system. By giving people access to only the data and resources necessary for their role, you also reduce the likelihood of misuse or lateral movement. In order to accommodate changing responsibilities and business needs, you should also regularly review and adjust access limitations.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encrypting data is recommended both during transmission and storage. This guarantees that unauthorized users cannot see the data even if they manage to get access to a device. A secure data plan must include encrypted databases and secure communications technologies.
Back up Critical Data
Backups are your safety net. You may thus set up an automated backup system that maintains copies both online and off. You should also regularly test your recovery process to ensure company continuity.
Monitor Network Activity

You can use real time monitoring Security Information and Event Management tools to detect abnormal behaviors and suspicious user activity. Moreover, you should couple them with threat intelligence feed and automated alerts to improve your incident response time.
Testing
Additionally, you can hire security experts to use controlled simulated assaults to test your defenses. Penetration testing might also reveal hidden flaws in your apps or infrastructure. Moreover, vulnerability scans may be used in conjunction with this to find and fix security vulnerabilities.
Secure Your Supply Chain
Some outside vendors may put your ecosystem in danger. As a result, you should ensure vendors adhere to security requirements and perform due diligence before onboarding them. Also, you should regularly assess their compliance.
Isolate Networks
Segmenting a network prevents unwanted access and viruses from spreading. Therefore, you may limit mishaps and lessen assaults by separating critical environments, like databases and financial systems, from general user access.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
You should be prepared for a cyberattack. Therefore, you should prepare a reliable response plan. In this plan, you should outline the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved. Furthermore, you should also establish communication protocols needed during a security breach.
Secure Remote Work
With more organizations supporting remote work, securing endpoints outside the traditional network perimeter is essential. Furthermore, you should ensure remote employees follow data handling policies.
Stay Informed About Emerging Trends
Cybersecurity changes quickly. Therefore, you should stay informed through threat intelligence reports and industry news. Also, you should engage with the cybersecurity community to recognize patterns and adapt defenses proactively.
Use Behavioral Analytics
Traditional security tools are based on signature based detection. Therefore, these tools can miss new threats. Behavioral analytics uses machine learning to understand user behavior and detect anomalies. Hence, this helps in identifying insider threats and compromised accounts early.
Secure APIs

APIs and web applications are common attack vectors for cyber attackers. This is because companies are moving towards microservices and cloud applications. Therefore, you should secure APIs by enforcing authentication and encrypted transmission.
Final Words
The complexity of cybersecurity threats is increasing. However, if you use the right techniques, you can remain safe. Additionally, you may reduce risks and increase resilience by fusing dependable technology with proactive defensive strategies.




