For ages, we have known that web applications are the prime target for cyber attackers. They attack a web application regardless of its size and nature. This makes every online service vulnerable to a wide range of attacks.
The graph below shows an excessive increase in the number of cyber attacks globally.
So, to tackle such attacks and protect web applications, we have a Web Application Firewall (WAF) that acts as a barrier between your application and malicious attacks. Such a firewall has become a necessity to keep your application and data secure from vulnerabilities and cyberattacks.
This article enlightens our readers about the web application firewall, its importance, features, and implementation approaches. Hence, it will lead to the implementation of a web application firewall on your application.
What is a Web Application Firewall?
The WAF, or web application firewall, is the first responder on web applications that protects them from common web-based threats and attacks. It protects the application from internet traffic and sits between a web application, network, and the internet, for monitoring, filtering, and blocking malicious traffic.
These firewalls are a common tactic used by web applications to deal with common security issues and protect systems from malware infections, impersonation, and zero-day exploits. Unlike traditional firewalls that protect the network layer, WAFs keep the application layer secure, which is the favorite target for cyber attackers.
Types of Web Application Firewalls
Three primary types of web application firewalls are implemented as per need. Let’s go through the types:
Network-based Firewall
Network-based firewalls are usually hardware-based. Such a firewall is installed locally to reduce latency. Moreover, in all the types of firewalls, it is the most expensive type and necessities storing and maintaining physical equipment.
Host-based Firewall
In this type, the firewall is fully integrated into the application’s software. Such firewalls are cost-effective compared to network-based firewalls and are more customizable. However, you’d better be ready, as it consumes extensive local server resources. This leads to a complex implementation process and higher maintenance costs.
Moreover, the machine that runs the host-based firewall requires customizations that take time and can be costly.
Cloud-based Firewall
Thirdly, we have a cloud-based firewall, which typically doesn’t require any upfront investment. All you have to do is pay a monthly or annual charge for a security-as-a-service subscription. This makes it a cost-effective firewall. Moreover, you can easily implement it.
Notably, the cloud-based firewall is updated regularly without any extra cost. However, while choosing a cloud-based firewall, look into its customization options and ensure it matches your requirements.
Features of Web Application Firewall
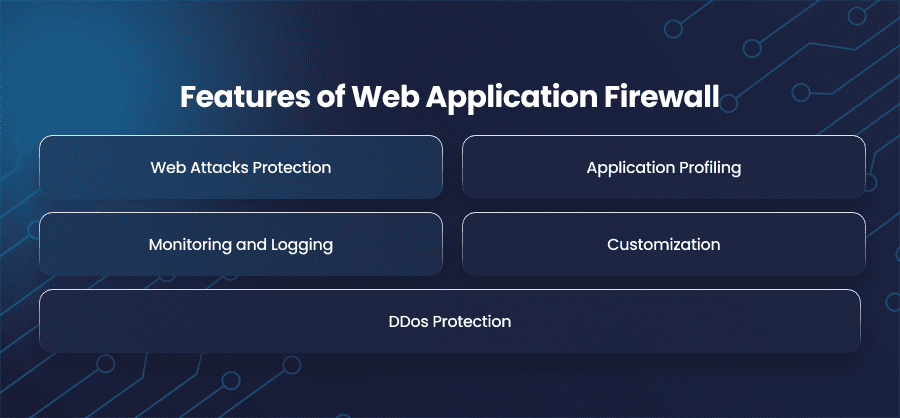
Before implementing any firewall on your web application, understand what WAF has to offer. Here are the core features of WAFs that persuade users to implement a firewall on their systems.
Web Attacks Protection
Implementing a firewall on your web applications protects your assets from web attacks, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting, cross-site forgery, and buffer overflow. Moreover, it also protects your system from common attacks such as HTTP request smuggling, remote file inclusion, etc.
Application Profiling
With a firewall installed on your system, it can analyze the structure of an application, including typical requests, URLs, values, and permitted data types. With this, the firewall is enabled to identify and block potentially malicious requests.
Monitoring and Logging
Moreover, WAF gives you a detailed traffic analysis and insights about potential security threats. It captures and stores the web application activity and performs security investigations and compliance. Moreover, you get real-time data on web traffic and security events.
Customization
You can implement a firewall on your terms. This means you can customize the behavior of a WAF according to your needs and prevent the blocking of desired traffic.
DDos Protection
For dealing with distributed denial of service attacks, you can integrate a cloud-based platform. Once the firewall detects a DDoS attack, it transfers the traffic to the DDoS protection platform, capable of handling large volumes of attacks.
Working of Web Application Firewall
A web application framework can be a service or a tool that examines the HTTP requests and applies specific rules. These rules specify which elements of the conversation are harmful and which are not.
GET and POST requests are the core components that a firewall examines. POST requests are used to submit data to a server for modifying its state, while GET requests are used to fetch data from the server.
The firewalls are also capable of analyzing PUT and DELETE requests that send data to a server for updating and requests for data deletion.
Approaches to Analyze and Filter Content
A web application firewall has three approaches to analyze and filter the content in the HTTP requests. These approaches are:
- Allowlisting
- Blocklisting
- Hybrid Security
Allowlisting
Firstly, the firewall denies all requests by default and only allows trusted requests. It provides a list of secure IP addresses. While blocking requires more resources than allowlisting.
However, the drawback you may witness of allowlisting is that it may block harmless traffic.
Blocklisting
The second approach is blocklisting. It uses preset signatures to block malicious traffic and protect web applications from vulnerabilities. It works by blocking requests that match specific criteria, patterns, indicating malicious activity. Moreover, this approach allows most of the traffic to pass through until something is flagged.
Hybrid Security
Finally, we have a hybrid security approach. This model uses elements of both allowlisting and blocklisting simultaneously to block what is malicious and vulnerable.
How a Web Application Firewall is Deployed?

Deploying a web application firewall depends on your specific requirements, threats, and application infrastructure. All things are considered before initiating the implementation of a firewall.
Here are the common deployment options for a web application firewall:
Inline Mode
A firewall can be deployed in line between the web application and the network. It intercepts every incoming request, inspects it as per the pre-defined rules, and allows or blocks it. This deployment option is very popular and extremely effective as it blocks the malicious content actively before it reaches the server.
Out-of-Band Mode
This mode doesn’t intercept or interrupt the traffic. Instead, it observes the copy of traffic silently and alerts the system upon any malicious activity. This mode doesn’t actively block threats, however is useful where latency is minimized or during the initial assessments.
Cloud-Based Firewall
Deploying a cloud-based firewall is also feasible for web applications. This involves redirecting traffic to the provider infrastructure via DNS changes. Moreover, this model is scalable and flexible for web applications with no need for on-premises hardware.
This deployment approach is extremely effective for cloud-hosted applications.
Appliance-Based Firewall
You can also install web application firewall appliances on-premises. These are physical devices within the network infrastructure that provide dedicated and localized protection for organizations with specific hardware requirements.
How to Implement a Web App Firewall – A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s go through the step-by-step guide for implementing a web app firewall.
Step 1: Assess Your Web Application Infrastructure
Firstly, you need to have a keen understanding of your application’s infrastructure. Identify all entry points, APIs, microservices, and user interactions. Moreover, map data flow and traffic sources for a deep understanding of the application.
Step 2: Define Security Requirements
Once done with the infrastructure, define the security requirements based on the nature of your application. Consider the sensitivity of the data your application covers. Don’t neglect relevant industry regulations. Moreover, asses the current threats that can attack your site.
Step 3: Choose the Right Web App Firewall
Thirdly, go through various firewall solutions. Look into their strengths and weaknesses. Understand what they offer, their overall cost, and level of security, support, and documentation. This will help you choose the best firewall type, aligning with your technical and business needs.
Step 4: Plan the Deployment
Once you choose a firewall solution, you need to plan your deployment strategy. For this, you need to understand the deployment approaches. Consider which approach suits your application’s infrastructure.
To minimize the disruption and false positives, it is always best to begin with a staging environment for testing and fine-tuning before deploying to production.
Step 5: Configure Rules and Policies
After deploying, you need to enable the default protection rules provided by the vendor. Later, you can customize these rules according to your application needs and business logic.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
Monitoring and optimization of your firewall is extremely important. For this, you can use real-time dashboards and alert systems that continuously monitor the incoming traffic and threats.
Plus, you also have to analyze the blocked requests to identify any false positives or negatives, and configure the set of rules accordingly.
Step 7: Conduct Regular Security Audits
Lastly, it is also important to make security checks a routine. Scan for vulnerabilities and perform penetration tests to evaluate the effectiveness of your web app firewall. Regular checkups help identify vulnerabilities and gaps and keep your firewall in top-notch form against new threats.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome
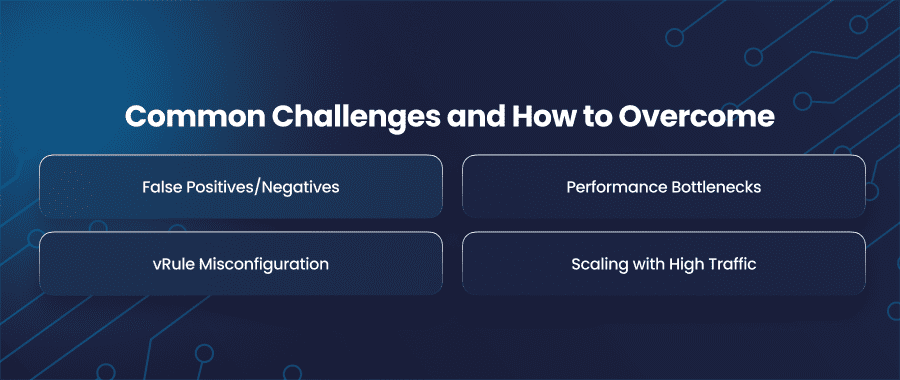
False Positives/Negatives
The first issue is of false positives and false negatives. To deal with this problem, one needs to use logging to identify misclassifications. Moreover, regularly reviewing and adjusting rules can also assist in this matter.
Performance Bottlenecks
Secondly, performance issues need to be addressed by choosing a web application firewall with minimal latency. Furthermore, optimizing the firewall’s configuration and managing the hardware resources can also help tackle this issue.
Rule Misconfiguration
Thirdly, there is a common challenge of rule misconfiguration that hinders the performance of the web application firewall. For this, you can use templates and pre-tested rulesets and involve developers in policy creation.
Scaling with High Traffic
Scaling with high traffic is also an issue. You can overcome this by using load balancing and auto-scaling firewall solutions.
Summary
So, with a web application firewall on your site, you make your site secure, protected from malicious attacks and vulnerabilities. With the rising threats, the firewall is not just a choice but a necessity to keep your assets secure. Whether you are a startup or an enterprise, understand the working and benefits of a web application firewall and implement it to keep your site up to modern standards.