According to a report, 50% of users of business management software report improvement in operational efficiency within a year of implementation. Moreover, 25% of SMEs are planning to increase their budgets for business management software. Hence, this goes to show the growing importance of software in business operations.
Businesses are integrating software into every aspect of their operations. Additionally, companies of all sizes may now compete internationally thanks to cloud platforms.
Ten ways that software is transforming corporate operations will be covered in this tutorial. Therefore, these insights will demonstrate how technology is changing organizations, regardless of whether you are an enterprise executive or the founder of a startup.
10 Ways Software is Transforming Business Operations
1. Automation of Routine Tasks
Automation is a fundamental component of business operations. Therefore, companies are turning to software automation to eliminate manual processes. A potent tool that helps companies automate rule based processes across departments is robotic process automation. RPA bots may simulate human behavior and communicate with digital systems across applications, handling everything from processing consumer refunds and updating CRM data to automatically creating reports and handling payroll.
Zapier and other workflow automation platforms are also being used by enterprises to streamline processes across several apps. For example, when a consumer fills out an online form, an automated procedure can update the CRM. It can notify the sales team in Slack.
AI automation is also becoming more popular. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can now handle more complex decision making activities, such as approving loan applications based on dynamic data or routing customer care inquiries to the appropriate department based on context.
Automation is also very important in supply chain activities. For instance, predictive inventory management systems adjust procurement strategies based on demand projections and automatically restock items as stock levels fall.
2. AI Decision Making
Nowadays, artificial intelligence is a key component of corporate strategy. It turns the long, intuitive process of decision making into a quick, data supported advantage. Organizations are now operating in a world of data overload, like collecting information from customers and markets at an unprecedented scale. However, raw data isn’t enough. AI bridges the gap by analyzing massive datasets in real time and recommending optimal actions with incredible precision.
AI tools like Salesforce Einstein are embedded across industries and functions. Predictive analytics is also being used by organizations to forecast sales performance and product demand. Additionally, natural language processing aids in the interpretation of survey data and customer evaluations in order to derive insightful information. Additionally, recommendation engines use user behavior to provide product or service suggestions. Furthermore, anomaly detection systems flag suspicious activity in cybersecurity.
Moreover, AI is also contextually aware. Unlike a traditional rule based system, AI models can learn from past outcomes and improve over time. As a result, decision making becomes more intelligent and flexible with every iteration. AI in retail dynamically modifies prices in response to competition behavior and inventory levels.
In logistics, it continuously recalculates delivery routes by considering traffic and delays. Moreover, in HR, AI can assist in matching the right candidate to the right role using machine learning models.
3. Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure has changed from a tech trend into a foundational pillar of modern business operations. Additionally, businesses from a variety of sectors are moving away from conventional on premises servers and toward more adaptable and affordable cloud infrastructures. Applications may now be hosted on platforms like AWS, which also make it possible to access mission critical systems remotely.
Scalability on demand is one of cloud infrastructure’s greatest benefits. Additionally, by removing the need for an upfront capital investment in expensive equipment, this flexibility allows companies to transition from a CapEx approach to an OpEx model.
Additionally, the development and implementation of software is being altered by cloud technologies such as serverless computing and microservices architecture. Businesses can split huge programs into smaller, independently deployable components that update continually by using tools like Docker.
Another significant benefit of cloud infrastructure is remote accessibility. Teams from several time zones may collaborate in real time anywhere there is an internet connection. This capability has enabled the utilization of hybrid work paradigms. As a result, businesses may operate and hire people more freely while still promoting teamwork.
Additionally, cloud providers assist companies in safeguarding sensitive data by providing strong security processes and compliance frameworks. Cloud solutions also provide regular backup.
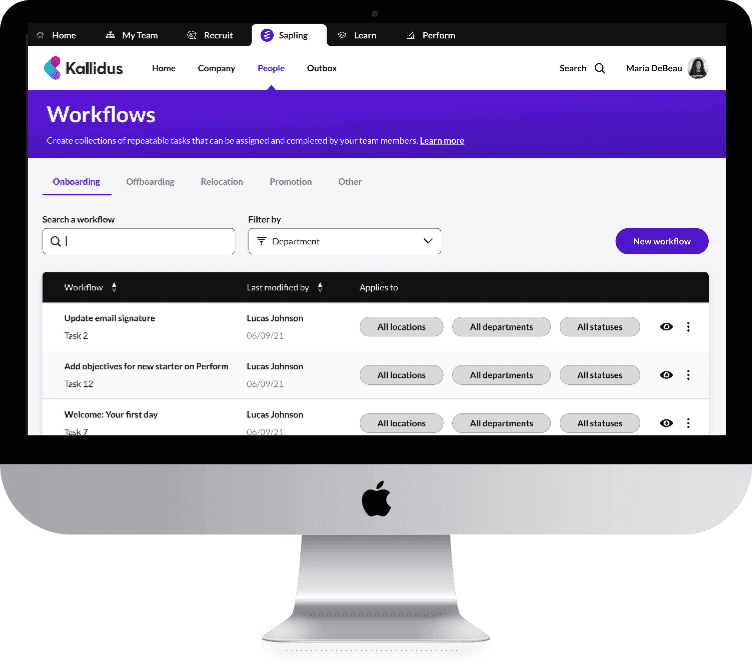
4. Collaboration Platforms
To keep team members connected and productive across time zones, businesses are increasingly relying on unified communication technologies. Tools like Notion are revolutionizing work by combining real time collaboration.
Unified platforms remove the need to continuously switch between different programs, in contrast to traditional solutions that function in silos. Within the same interface, staff members may communicate and even incorporate external technologies like CRMs and automated procedures. This guarantees that teams remain in sync regardless of their location and lessens friction in routine work.
One of the key strengths of these platforms is their real time collaboration capabilities. Teams can co edit and monitor project progress live. Activity streams and notifications keep everyone informed and less likely to miss communications.
Additionally, these platforms are becoming the focal point for interaction and corporate culture. Remote teams may maintain a sense of community and belonging by using unified collaboration tools like surveys and informal team forums. Many systems now include integrated analytics that enable executives to track engagement and identify bottlenecks.
Additionally, essential to contemporary collaboration platforms are security and compliance. Businesses may guarantee the protection of sensitive data while adhering to regulations by using features such as end to end encryption. These systems’ enterprise suitability is further enhanced by integration with identity providers and data governance solutions.
5. CRM and ERP Systems
Customer Relationship Management and Enterprise Resource Planning systems are no longer optional software tools; they are strategic assets driving operational excellence. Moreover, these platforms are at the heart of how businesses manage internal operations and external relationships, and automation across departments.
CRM systems such as HubSpot have changed far beyond simple contact management. These days, they function as cognitive engines that monitor every contact throughout the client experience, from engagement and post-purchase support to lead generation and sales conversion. These platforms provide a 360 degree picture of each consumer by integrating with eCommerce and marketing automation solutions. This comprehensive visibility allows sales and support teams to personalize communication.
Integration is one of the biggest advantages of contemporary CRM and ERP systems. In the past, departments operated autonomously, which frequently led to inaccuracies and duplicate data. CRM and ERP platforms may readily interface with one another and with third party apps by using APIs and native connectors. This connection removes redundancies and guarantees that data moves freely throughout the company.
These solutions are now safer and accessible thanks to cloud deployment. Companies may use CRMs and ERPs from any location with internet access and at a lower initial cost. These systems’ mobile accessibility and automatic upgrades make them perfect for the scattered and dynamic nature of modern business.
6. Zero Trust Frameworks
Businesses are using Zero Trust security frameworks to safeguard their data and digital infrastructure as cyber threats increase. Furthermore, Zero Trust follows the maxim “never trust, always verify.” It requires strict identification verification for every user and device, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s perimeter.
In the age of dispersed teams and remote work, this strategy has become essential as the traditional idea of a secure network barrier is no longer relevant. Additionally, workers access systems from different places, and hackers frequently take advantage of this intricacy. By regularly authenticating users and giving access based on context, Zero Trust mitigates these dangers.
Modern software solutions like Microsoft Defender for Identity offer comprehensive Zero Trust capabilities. These include multi factor authentication and network segmentation. Together, these tools monitor user activity in real time and restrict access dynamically to minimize the attack surface.
Granular access management is one of Zero Trust’s most potent features. Users are given the minimal amount of access required for their function rather than extensive permissions. For example, a member of the marketing team may have access to campaign data but not financial information.
Zero Trust architectures also enhance regulatory compliance. Zero Trust architectures assist fulfill strict data protection rules in industries like banking and government by offering thorough audit trails and encryption at every level.
7. Workflow Integration with API Ecosystems
Businesses no longer have to rely solely on monolithic software platforms. Instead, businesses are embracing the flexibility of API driven ecosystems to build integrated processes across tools and platforms.
Businesses may design bespoke workflows that are specific to their requirements by using APIs. For example, an eCommerce website’s APIs can initiate a sequence of automatic operations when a consumer places an order.
Furthermore, dismantling silos is where API based integrations truly provide value. In the past, departments worked independently, utilizing disparate systems that were ineffective at communicating with one another. This led to ineffective manual handoffs and fragmented data. Therefore, companies may guarantee accurate and unrestricted data flow between systems by establishing an integrated digital ecosystem.
Additionally, real time processes are supported with API connectors. For example, marketing teams may instantly sync campaign data from social media sites into CRMs, while operations teams can get real time order updates from logistical partners. This seamless connectivity allows teams to respond faster.
8. Low Code Platforms
The use of low code and no code platforms to create robust apps and automate processes without the need for traditional programming knowledge has increased due to the need for quick digital transformation. By offering user friendly drag and drop interfaces and visual builders that significantly cut down on the time and expertise needed to deploy workable digital solutions, these platforms have democratized software development.
Business users and operations teams may create everything from internal dashboards and mobile applications to automated approval processes and consumer portals using low code platforms like Microsoft Power applications and no code solutions like Webflow.
One of the biggest advantages of these platforms is agility. Low code and no code platforms provide that speed, enabling rapid iteration and easy adjustments without deep development cycles.
9. Customer Support with Chatbots
Businesses are using AI chatbots and virtual agents as a key part of their customer experience strategy in order to fulfill growing consumer expectations and manage growing support loads. By offering support via platforms like mobile applications, these intelligent bots are changing how businesses interact with their users.
Compared to earlier script based systems, modern chatbots are significantly more advanced. Intercom is one example of a tool that can comprehend user intent and sustain contextual discussions.
Scalability is one of the biggest benefits of chatbots. Chatbots can service thousands of consumers at once without any delays, unlike human support teams who need more staff to accommodate the rising demand.
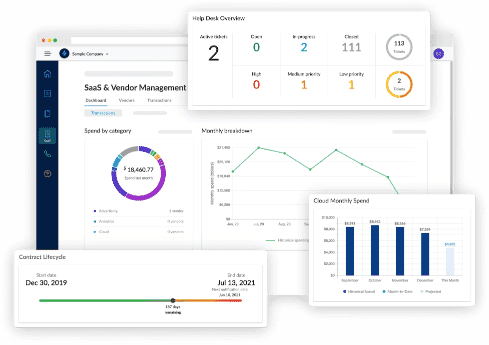
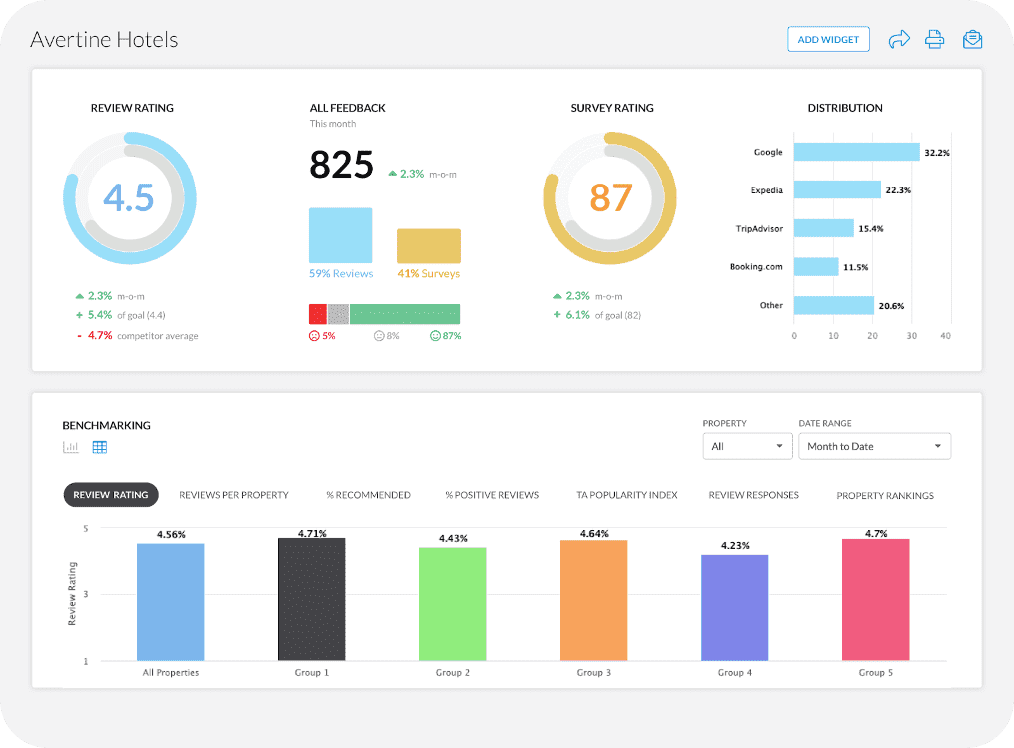
10. Data Visibility and Dashboards
The most precious resource a company can possess is data. But how it’s accessed and understood determines its actual potency. For this reason, businesses are spending a lot of money on data visualization technologies and real time dashboards.
Businesses can now compile data from many sources and display it using dashboards that can be customized thanks to contemporary platforms like Tableau. Even non technical users may easily see patterns and abnormalities thanks to these dashboards, which convert complicated data into charts.
Interactivity is one of the most potent characteristics of contemporary dashboards. Users can alter views based on their function or goal and dive down into certain data pieces.
Final Words
By promoting automation and more thoughtful decision making, software is revolutionizing business processes. By enabling businesses to operate more quickly and develop constantly, these solutions transform technology into a real competitive advantage.